Category: Letter B
-
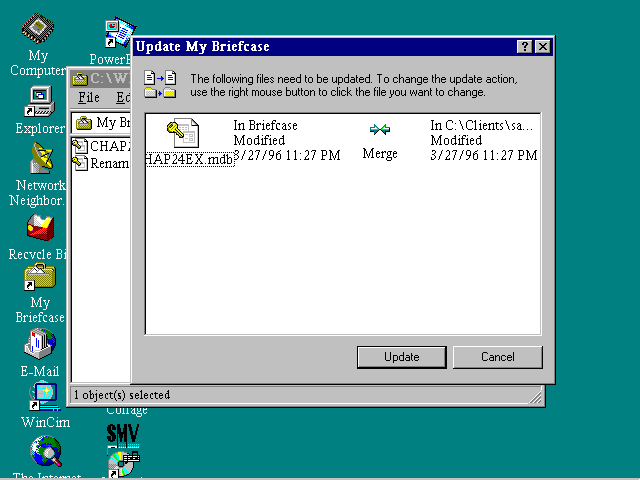
Briefcase (Microsoft Windows)
Briefcase was a feature of Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000 that is typically used to enable mobile users to copy and synchronize files between a desktop and a portable computer so that they can easily copy and work on files at home or on the road without creating version…
-

Backup
In this article, we will delve deeply into what Backup is, discuss the various backup strategies available, examine the different types of backup, and analyze how backup operations affect the archive attribute of files. The goal is to provide a comprehensive overview of best practices for protecting business data and ensuring operational continuity in any…
-
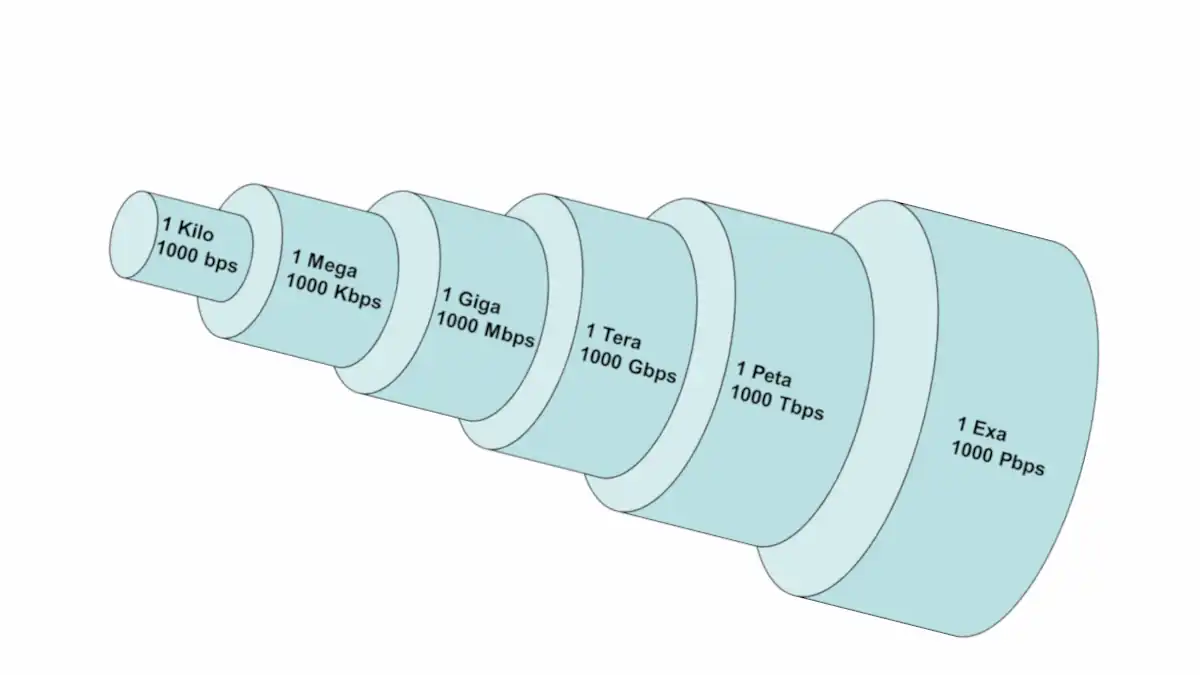
Bandwidth Explained!
In general, Bandwidth is the difference between the highest and lowest frequencies in a given range of frequencies for an analog signal. For example, if the lowest and highest frequencies a telephone line can carry are 300 Hz and 3300 Hz, the telephone line can accommodate a bandwidth of 3300 – 300 = 3000 Hz,…
-
Boot.ini
Boot.ini is a hidden and read-only text file on the root of the system partition of that is used to create the boot loader menu.
-
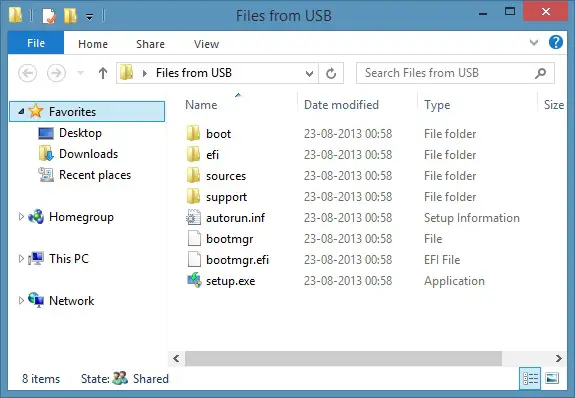
Boot Files
Boot Files are files needed to boot an operating system on a computer.
-
Backup Site Controller (BSC)
Explore the outdated yet educational concept of Backup Site Controller (BSC) in Microsoft Message Queue Server (MSMQ) environments. Understand how modern solutions have replaced it for better fault tolerance and load balancing.
-
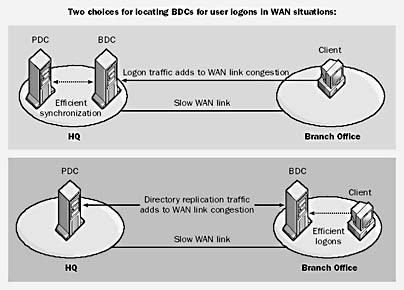
Backup Domain Controller (BDC)
A Backup Domain Controller is a Microsoft Windows NT domain controller containing a read-only copy of the master domain directory database located on the primary domain controller (PDC).
-
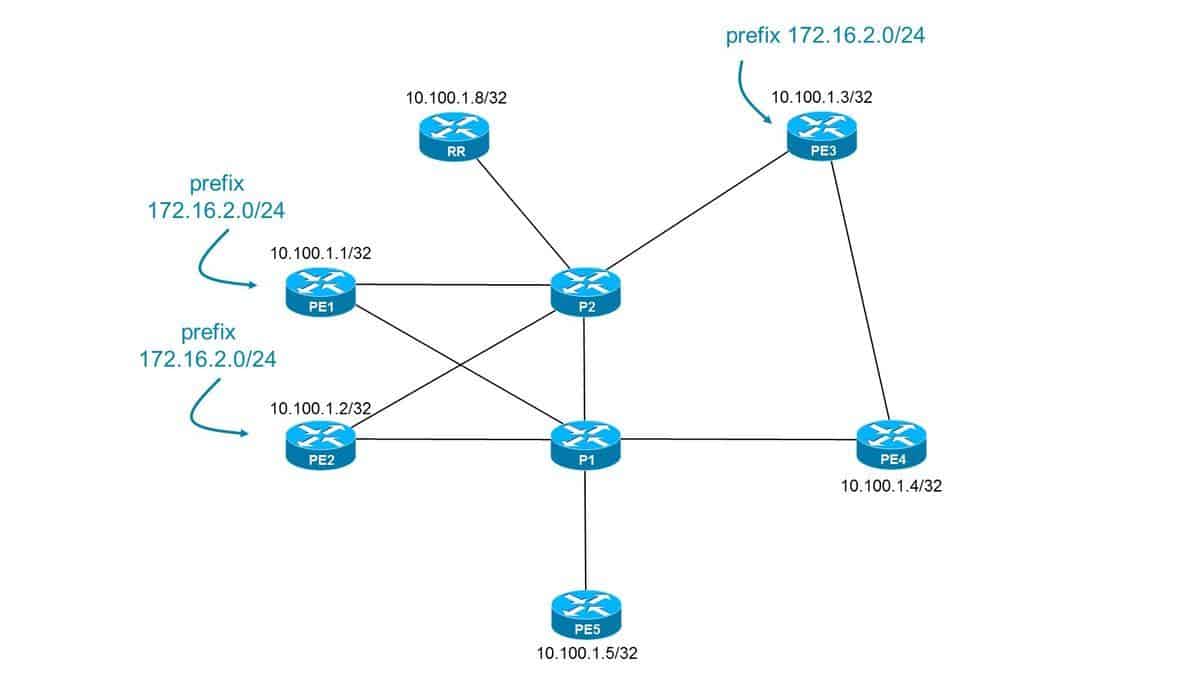
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is a standard TCP/IP protocol based on the distance-vector routing algorithm that enables groups of routers to share their routing information in an efficient manner.
-
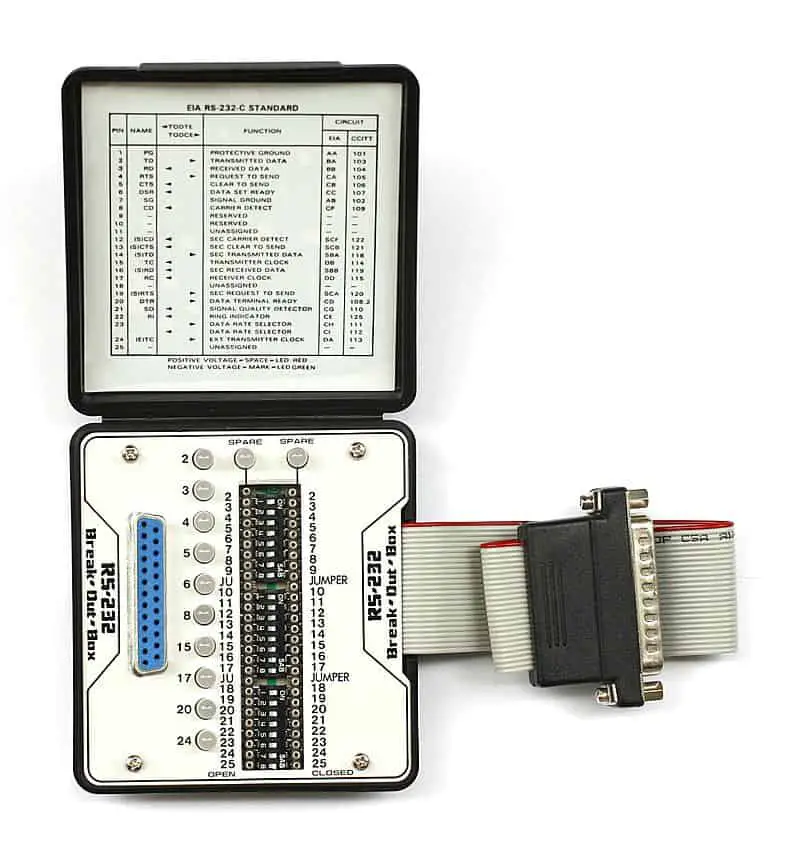
Breakout Box
Breakout Box is a troubleshooting tool used to determine the wiring of an RS-232 interface on a networking device or computer.