Category: Network Protocols
-
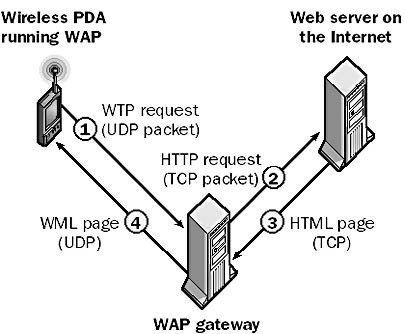
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
Wireless Application Protocol, or WAP, is a set of technologies developed by a consortium of mobile telephony equipment vendors that is designed to bring Web content to wireless handheld communication devices such as Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones.
-

Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP)
SLIP is an industry-standard protocol developed in 1984 for UNIX environments that supports TCP/IP networking over serial transmission lines.
-

Pass-Through Authentication
Pass-Through Authentication is a method of performing authentication to a domain controller that resides in a trusted domain.
-

Line Coding
Line Coding is a method of placing digital signals on a wire.
-
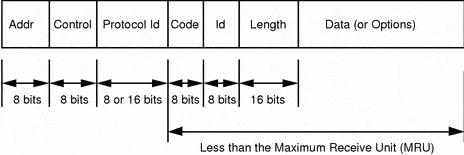
Link Control Protocol (LCP): Mastering PPP Link Management
Uncover the essentials of Link Control Protocol (LCP), a crucial subprotocol of PPP for effective network link management.
-
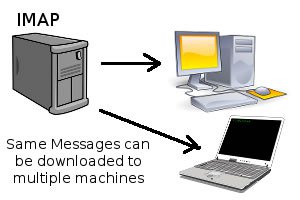
Internet Mail Access Protocol version 4 (IMAP4)
IMAP4 stands for Internet Mail Access Protocol version 4, is an Internet standard protocol for storing and retrieving messages from Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) hosts.
-

Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP)
Explore the essentials of Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP), its types, and applications in efficient network routing.
-

Handshaking (in Networking)
Handshaking is the process that establishes communication between two networking devices.
-
Full-Duplex Ethernet: Doubling Network Efficacy
Full-Duplex Ethernet is an emerging type of Ethernet that supports full-duplex communication between stations on the network.
-

DNS Client: Navigating the Digital Sea
DNS Client is a client machine configured to send name resolution queries to a DNS server. A DNS client is also called a resolver. When a client needs to resolve a remote host’s name into its IP address, it sends a request to the DNS server, which returns the IP address of the remote host.…
-

Understanding the CHAP Protocol: Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, or CHAP, is an encrypted authentication scheme in which the unencrypted password is not transmitted over the network.
-
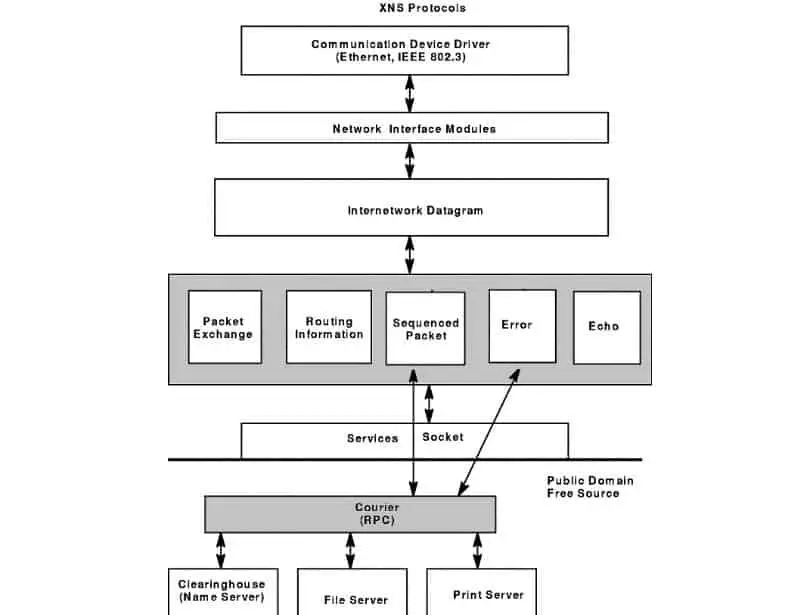
Xerox Network Systems (XNS)
Xerox Network Systems is a suite of networking protocols developed by Xerox Corporation’s Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) in the early 1980s.