Category: Letter H
-

High-Performance Routing (HPR): Revolutionizing Network Communication
Conceived to address the growing demands for efficiency and reliability in network communication, HPR marks a significant departure from traditional routing methodologies.
-

HTTP/2 Multiplexing: Revolutionizing Web Communication
By allowing multiple requests and responses to be sent simultaneously over a single TCP connection, HTTP/2 multiplexing dramatically improves web performance, reducing latency and optimizing resource utilization.
-
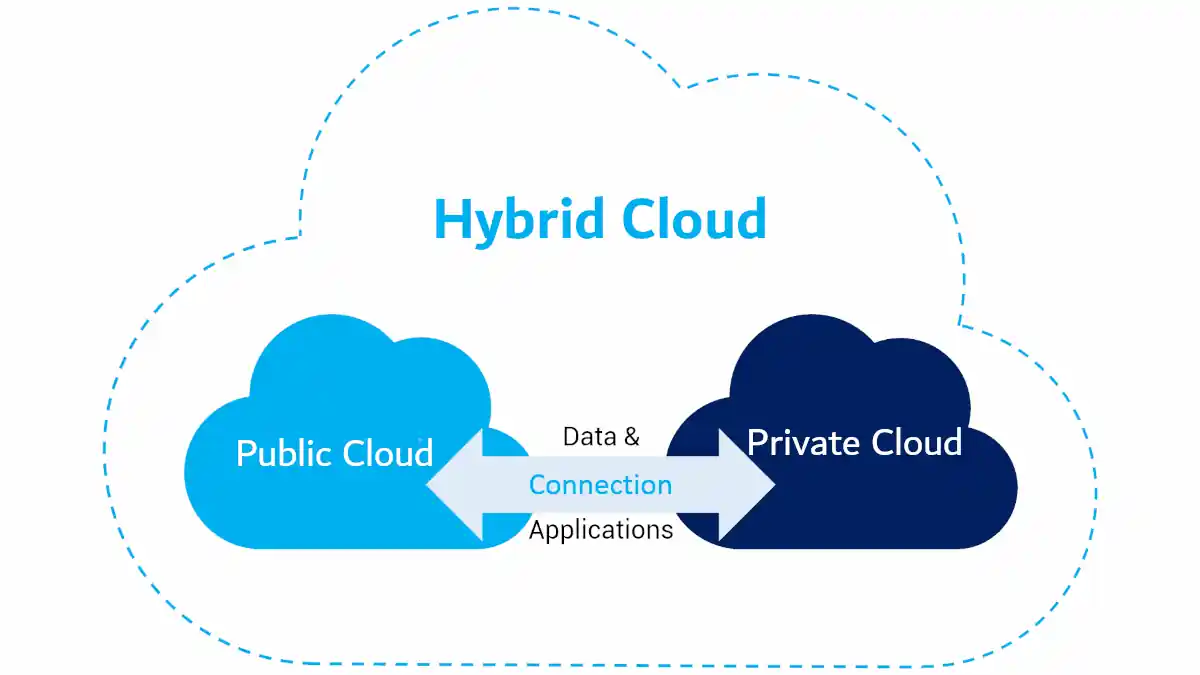
The Future of Hybrid Cloud: Integrating AI for Optimized Networking
Explore the future of Hybrid Cloud as we delve into integrating AI for optimized networking. Discover how intelligent systems can revolutionize cloud management and security.
-

Securing Your Website: A Guide to HTTP Header Vulnerabilities
Learn about the common security risks associated with HTTP headers. This guide explores vulnerabilities that every website owner should be aware of, and how to secure your website against them.
-

Hackathon: Innovating Solutions at Lightning Speed
Dive deep into the exciting world of hackathons – where innovation meets collaboration, all under the ticking clock.
-

History of IPv6 and Its Key Features
Learn the history of IPv6. In 1992 that IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) became aware of a global shortage of IPv4 addresses.
-
HyperTerminal
HyperTerminal is a communication utility included in Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, and Windows 2000 that provides terminal access to remote computers using a modem.
-

Understanding HTTP Keep-Alives
HTTP Keep-Alives is an enhanced version of HTTP persistent connections supported by Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS). HTTP Keep-Alives allow a client Web browser to keep connections open with the Web server instead of closing them after the request has been answered and reopening them for each new Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) request, which consumes…
-
HTTPS
HTTPS is a protocol developed by Netscape for secure transmission of Web content over the Internet. HTTPS is another name for Netscape’s implementation of the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol that functions as a subprotocol to the application layer (layer 7) protocol, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
-
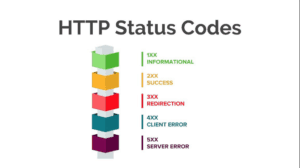
HTTP Status Codes
HTTP Status Codes are three-digit codes that Web servers return in response to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) requests sent by Web browsers. They are also known as HTTP error codes because most of them signify some sort of error condition. In this page The HTTP status code is one of the first pieces of information…
-

Http Cookie
In Internet technologies, a cookie is a text file that a Web server saves on a client machine during a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) session. HTTP Cookies are used to record information about the client’s usage patterns, including the date and time the client visited the site, which pages were accessed, Web browser preferences, and…
-
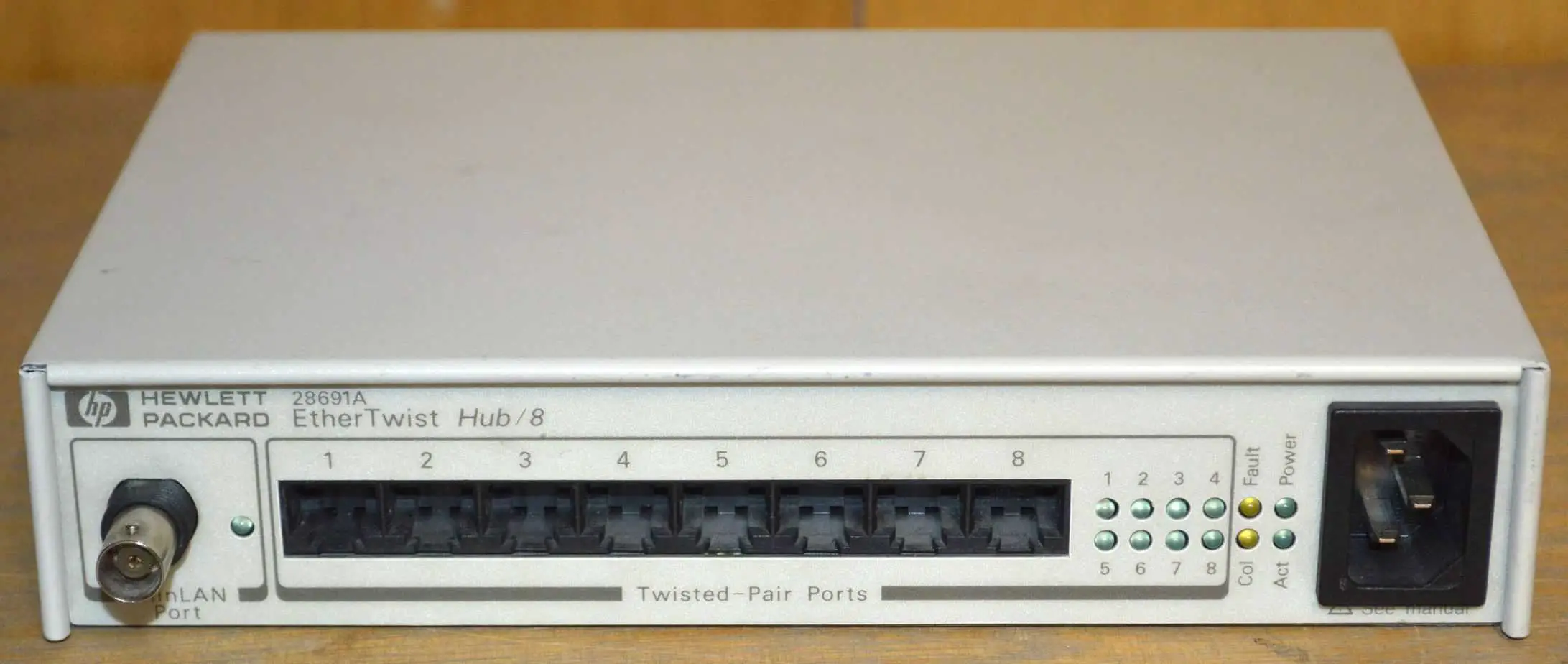

Hub
Hub also called a repeater hub, is the basic networking component used in traditional 10-Mbps Ethernet networks to connect network stations to form a local area network (LAN).