Category: Network Protocols
-
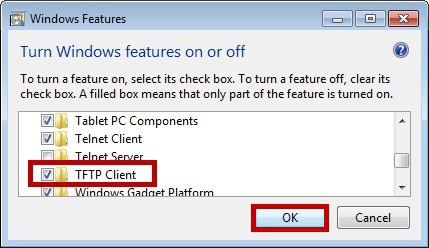
TFTP
Explore TFTP: A concise guide to Trivial File Transfer Protocol, its functions, implementations, and modern network applications.
-
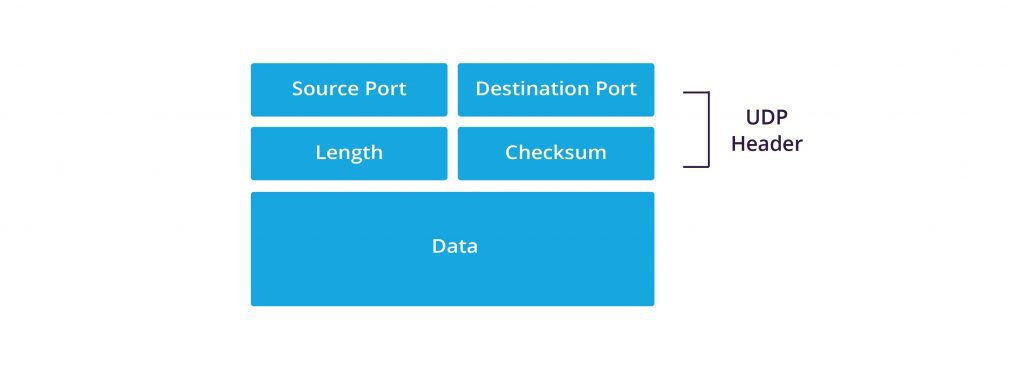
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
User Datagram Protocol, known as UDP, is a TCP/IP transport layer protocol that supports unreliable, connectionless communication between hosts on a TCP/IP network.
-

Common Internet File System (CIFS): Network File Sharing Made Easy
Unlock the capabilities of CIFS, the protocol at the heart of network file sharing and collaboration. Dive into its functionalities, uses, and impact.
-
Static Routing: A Comprehensive Guide
Static Routing is a routing mechanism that is handled by the Internet Protocol (IP) and that depends on manually configured routing tables.
-
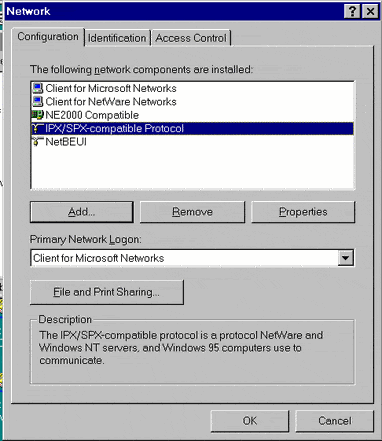
IPX/SPX – Compatible Protocol
IPX/SPX stands for Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange is a set of network protocols that provide packet switching and sequencing for small and large networks, used initially on networks using the Novell NetWare operating systems.
-
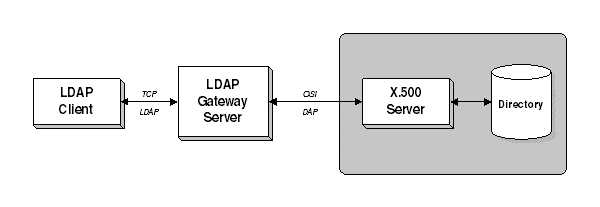
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an Internet protocol for accessing and updating information in an X.500-compliant directory.
-
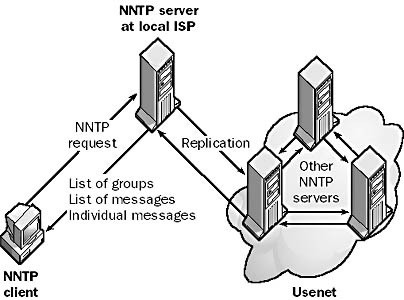
Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)
NNTP stands for Network News Transfer Protocol is an Internet standard protocol that governs the interaction between Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) servers (news servers) and NNTP clients (news readers).
-

Network Frame
Explore the essentials of network frames: their structure, role in data transmission, and pivotal function in the OSI Model’s data-link layer.
-
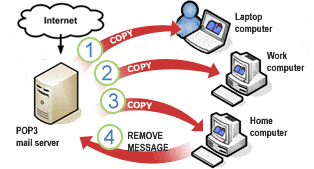
Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3)
Explore the ultimate guide to POP3: Post Office Protocol version 3. Learn about its history, functionality, advantages, disadvantages, and more!
-
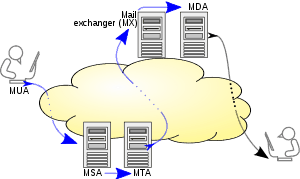
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is a standard application-layer protocol for delivery of e-mail over a TCP/IP internetwork such as the Internet.
-
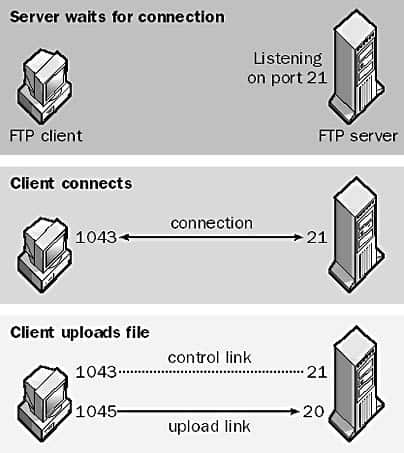
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol is an Internet standard application-level TCP/IP protocol that can be used for transferring files between hosts on a TCP/IP internetwork.
