In the vast universe of networking, the arteries that keep the data flowing are often made of a familiar, yet crucial material: copper cabling. This ubiquitous networking medium has powered our communication systems for decades. But what makes copper cabling the backbone of so many networks? And how has it evolved to meet the ever-increasing demands of the digital age? This article dives into the world of copper cabling, uncovering its significance in networking and exploring its multifaceted role in connecting the world. Are you ready to unravel the story behind the wires?
Table of Contents:
- What is Cooper Cabling?
- History and Evolution of Copper Cabling
- Types of Copper Cabling
- Technical Specifications and Standards
- Copper Cabling in Modern Networking
- Practical Considerations
- Future of Copper Cabling
- References
1. What is Cooper Cabling?
Copper cabling, one of the two primary types of physical cabling media used in networking (the other being fiber optics), stands as a cornerstone of modern communication infrastructure. It consists of copper wires that transmit electrical signals, which are used to convey data across network devices. The use of copper for cabling is due to its excellent electrical conductivity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of networking applications.
Key Characteristics of Copper Cabling
- Electrical Conductivity: Copper’s high electrical conductivity enables efficient transmission of signals with minimal loss, which is crucial for maintaining data integrity over distances.
- Flexibility: The malleable nature of copper allows cables to be easily bent and routed through tight spaces, a critical feature in complex network installations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other materials like fiber optics, copper is generally more affordable, both in terms of initial deployment and maintenance.
Common Uses in Networking
Copper cabling is extensively used in various networking environments, from small office LANs to large data centers. It supports a range of applications, including Ethernet connections, telephony systems, and broadband internet access.
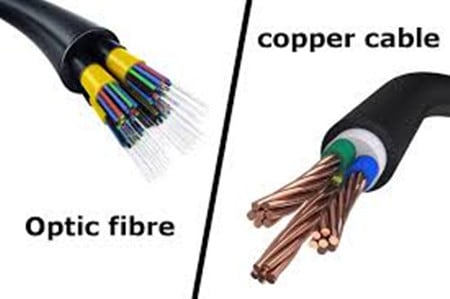
Types of Copper Cabling
The most common forms of copper cabling in networking include twisted pair cables, such as Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), and coaxial cables. Each type is designed for specific use cases and environments, offering different levels of performance and protection against electromagnetic interference.
In summary, copper cabling remains a vital component in the networking world, offering a reliable and cost-effective solution for a wide range of data communication needs. Its continued evolution and adaptation to new technologies underscore its enduring relevance in an increasingly connected world.
2. History and Evolution of Copper Cabling
The Early Days
Copper cabling’s journey in networking began with the invention of the telegraph in the early 19th century. Copper’s excellent conductivity made it the material of choice for these early communication systems. The subsequent invention of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876 further cemented copper’s role in communication technologies.
Twisted Pair Cables
- 1880s: The concept of twisting copper wires into pairs was introduced to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), a significant innovation that paved the way for more reliable communication.
- 20th Century: The widespread adoption of twisted pair cabling in telephone networks laid the groundwork for its eventual use in computer networking.
The Emergence of Categories
- 1980s and Beyond: The development of Ethernet in the 1980s required more structured cabling solutions. This led to the categorization of twisted pair cables based on performance characteristics like data transmission speed and bandwidth.
- Cat3 to Cat6a: Over the years, categories such as Cat3, Cat5, and Cat6 emerged, each offering improvements in terms of speed and bandwidth. Cat5e and Cat6a, for example, were developed to support faster data rates and higher frequencies.
Modern Usage
Today, copper cabling is ubiquitous in LANs and other networking environments. Despite the rise of fiber optics and wireless technologies, copper cabling’s adaptability has allowed it to remain relevant, evolving with advancements like Power over Ethernet (PoE) and higher-speed Ethernet standards.
3. Types of Copper Cabling
Twisted-Pair Cabling
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP):
- Usage: Most common in LANs and telephony.
- Categories: Ranges from Cat3 (used in older telephone systems) to Cat6a (used in modern Ethernet networks). See article: Difference between Cat5 and Cat6 cabling.
- Characteristics: Lacks additional shielding, making it thinner and more flexible but more susceptible to EMI.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
- Usage: Used in environments with significant EMI.
- Categories: Similar to UTP, but with additional shielding for each pair or the cable as a whole.
- Characteristics: Better protection against EMI, but thicker and less flexible than UTP.
Category Breakdown:
- Cat5 and Cat5e: Standard for Ethernet and telephone, supporting speeds up to 100 Mbps and 1 Gbps, respectively.
- Cat6 and Cat6a: Higher performance, with Cat6 supporting up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances and Cat6a over longer distances.
Coaxial Cabling
- Usage: Previously dominant in cable TV systems and early Ethernet networks.
- Types:
- Characteristics: Consists of a central copper conductor surrounded by insulation, a metallic shield, and an outer cover. Offers better protection against EMI than twisted pair cables.
Copper cabling, in its various forms, continues to be a versatile and vital component of networking infrastructure, adaptable to both legacy systems and modern high-speed networks.
4. Technical Specifications and Standards
Technical Specifications of Copper Cabling
Copper cabling in networking is characterized by various technical specifications, including data rate, bandwidth, and frequency, which differ across the different categories of cables. For instance:
- Category 5 (Cat5) Cable: Offers a bandwidth of 100 Mbps and was a standard for Ethernet and telephone networks.
- Category 6 (Cat6) and 6A (Cat6A) Cables: Designed for higher performance, with Cat6 supporting data transmission rates up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances, and Cat6A offering better performance over longer distances.
Standards by EIA and TIA
The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) and the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) have set standards for copper cabling to ensure compatibility and performance across different manufacturers’ products. These standards have evolved over time, with the introduction of new categories to meet the advancing requirements of network data transmission.
ANSI/TIA 568 C.2 Standard
This standard, published by TIA and accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), defines the categories of shielded and unshielded twisted pair cable systems. It includes specifications for signal bandwidth, insertion loss, and cross-talk, with higher category numbers corresponding to cable systems suitable for higher rates of data transmission. The current revision of this standard includes categories up to Cat8, which is suitable for 2,000 MHz.
The standard also defines structured cable system topologies and the pin-to-pair assignments for connectors, ensuring that cables are compatible and function correctly across different networking setups.
5. Copper Cabling in Modern Networking
Current State of Copper Cabling
Despite the emergence of fiber optic cabling and wireless technologies, copper cabling remains a staple in many network infrastructures, particularly in local area networks (LANs). Its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and suitability for a wide range of applications make it a practical choice for many organizations.
Comparison with Fiber Optic Cabling
While fiber optic cabling offers higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances without signal degradation, copper cabling is often preferred for its lower cost and flexibility, especially in shorter-distance applications. However, the higher susceptibility of copper cabling to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and its limited range compared to fiber optics are notable drawbacks.
Role in Data Centers and Enterprises
In data centers and enterprise settings, copper cabling is commonly used for connecting servers, switches, and other networking equipment. It supports technologies like Power over Ethernet (PoE), which allows devices to receive power and data over the same cable, simplifying infrastructure and reducing costs.
Challenges in High-Speed Networks
As network demands continue to grow, the limitations of copper cabling in terms of bandwidth and data transmission rates become more apparent. Advancements in copper cabling technology are ongoing to meet these challenges, but in some high-speed, high-bandwidth scenarios, fiber optic cabling may be a more suitable choice.
6. Practical Considerations
When deploying copper cabling in a network, several practical considerations must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): The most common choice in LAN environments, UTP cables are more affordable and easier to install due to their flexibility. However, they are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can be a concern in environments with heavy electrical equipment.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): STP cables include a shielding layer that provides additional protection against EMI. This makes them suitable for industrial environments or areas with high EMI. However, STP cables are more expensive and less flexible, making installation and handling more challenging.
Considerations for Installation
- Cable Length: Ensure that cable runs do not exceed the maximum recommended lengths (typically 100 meters for Ethernet over twisted pair) to avoid signal degradation.
- Environmental Factors: Consider environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to interference when choosing cabling types.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhere to ANSI/TIA and EIA standards to ensure compatibility and performance, especially when integrating with existing network infrastructure.
- Proper Termination: Ensure cables are terminated correctly to avoid issues like cross-talk and impedance mismatches, which can degrade network performance.
Impact of Shielding on Performance and Cost
- Performance: While shielding can improve performance by reducing EMI, it may not be necessary for all environments, and the added materials can increase the overall cost of the cabling solution.
- Cost Implications: The choice between UTP and STP can have significant cost implications, not only in terms of the cabling itself but also regarding installation and maintenance.
7. Future of Copper Cabling
Adaptation to Emerging Technologies
Copper cabling has shown remarkable adaptability, evolving to meet the demands of newer technologies like PoE and higher-speed Ethernet. This adaptability suggests that copper cabling will continue to play a significant role in network infrastructures.
Competition with Fiber Optics and Wireless
While fiber optic cabling offers higher bandwidth and is preferable in certain high-speed applications, copper cabling remains more cost-effective for many uses. Wireless technologies are advancing but still rely on wired backbones for critical network segments.
Innovations in Copper Cabling
Continued innovations in copper cabling, such as improvements in shielding and conductor quality, could extend its usability in higher-bandwidth applications. Technologies like G.fast, which enable faster data rates over copper lines, illustrate the potential for continued relevance.
Potential Challenges
The main challenges for copper cabling include bandwidth limitations and susceptibility to EMI. As data transmission requirements increase, the industry may see a gradual shift towards more fiber deployments in certain scenarios.
Conclusion
Copper cabling is likely to remain a mainstay in networking infrastructure due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and ongoing innovations. However, the increasing demand for higher bandwidth and lower latency may see a complementary rise in the use of fiber optics and wireless solutions in certain sectors.
8. References
- “Copper Cable in Networking: An Overview” – Enconnex Blog
- “Networking Fundamentals” by Richard M. Roberts
- RFC 1180 – “A TCP/IP Tutorial”
- “Data Communications and Networking” by Behrouz A. Forouzan