When we talk about digital communication, the concept of a ‘destination address’ is fundamental. It’s a term that resonates not just with network professionals but also with anyone curious about how information travels across networks. This article dives deep into the intricacies of destination addresses, unraveling their roles, formats, and significance in network communications. From the basics of IP addressing to the complexities of routing data across global networks, we’ll explore every facet of destination addresses.
This guide offers valuable insights and detailed explanations to enhance your understanding of this key component in the world of digital communication.
Table of Contents:
- What is a Destination Address?
- Role of Destination Address in Networking
- Destination Address vs. Source Address
- Formats and Protocols
- Destination Address in Different Network Topologies
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion
- References

1. What is a Destination Address?
destination address in the context of networking is a unique identifier used to determine the final recipient of a data packet within a network. In simpler terms, it’s like the ‘address’ on a postal letter, guiding where the information should be delivered in a digital network. This address ensures that data transmitted over a network, such as the internet or a local network, reaches the correct device or network interface.
The destination address is used by hosts on the network to determine whether the packet or frame is intended for them or other hosts. The destination address is also used by routers to determine how to forward the packet or frame through an internetwork.
Types of Destination Addresses
Destination addresses come in different forms, catering to various networking needs:
- Unicast Addresses: These addresses target a single specific device on a network. Data packets sent to a unicast address are intended for one recipient only. For example, when you send an email, it goes to a unicast address.
- Broadcast Addresses: Used in local networks (LANs), broadcast addresses allow the transmission of a data packet to all devices within the network segment. It’s akin to making an announcement in a room full of people.
- Multicast Addresses: These are used to send a single data packet to a group of recipients. Different from broadcast, multicast addresses target a specific set of devices, like a TV channel being broadcast to multiple televisions tuned to that channel.
Network sniffer
You can see the destination address of a packet or frame by using a network sniffer device such as Network Monitor, a tool included with Microsoft Systems Management Server (SMS). Network Monitor displays destination addresses in both ASCII and hexadecimal form.
2. Role of Destination Address in Networking
How Destination Addresses Enable Data Transfer
Destination addresses are fundamental in the process of data transfer across networks. When data is sent over a network, it is broken down into smaller units called packets. Each packet contains the destination address, which network routers and switches use to determine the correct path through the network. This system ensures that data packets find the most efficient route to their intended destination.
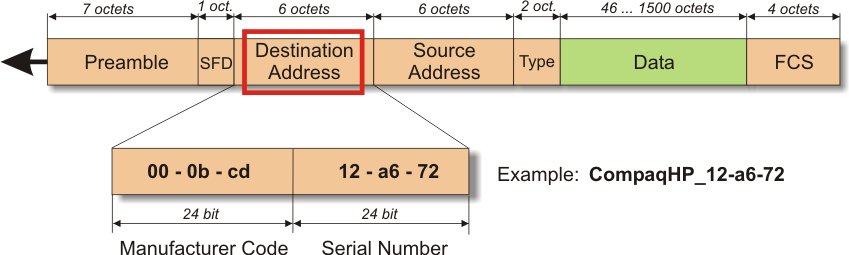
Understanding IP Addressing and Routing
- IP Addressing: The most common type of destination address is the IP (Internet Protocol) address. IP addresses are unique to each device on the internet or a local network. They come in two standards: IPv4, with a format like
192.168.1.1, and IPv6, a newer standard to cater to the growing number of internet devices. - Routing: This is the process of moving packets across a network from the source to the destination. Routers use the destination address to decide where to forward the packet next. Through a series of networks, each router reads the destination address and directs the packet until it reaches its final destination.
3. Destination Address vs. Source Address
Comparative Analysis
The destination address and source address in a data packet serve different, yet complementary, roles:
- Destination Address: This is the address where the data packet is being sent. It tells the network the final stop for the packet. It’s akin to the address you’d write on an envelope.
- Source Address: Conversely, the source address indicates where the data packet originated. This is like the return address on an envelope, providing information on where to send responses or acknowledgements.
Both addresses are essential for the successful delivery and response in network communications.
Synergy in Data Transmission
The interplay between destination and source addresses facilitates efficient and reliable data transmission:
- Routing and Delivery: Routers and switches use the destination address to forward data packets through the network, while the source address ensures that any return communication or data can be sent back to the correct sender.
- Error Handling and Network Management: Source addresses help in identifying points of failure or traffic bottlenecks, as they provide a clear trail back to the origin of the data.
4. Formats and Protocols
IPv4 and IPv6 Address Formats
- IPv4: This is the most widely used IP address format, consisting of four numerical octets separated by periods (e.g.,
192.168.1.1). Despite its widespread use, IPv4 faces limitations in address availability due to the sheer number of devices connecting to the internet. - IPv6: Developed to address the limitations of IPv4, IPv6 utilizes a longer address format, consisting of eight groups of hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (e.g.,
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). This format significantly increases the number of available addresses, accommodating the expanding internet infrastructure.
MAC Addresses in Local Networks
- MAC Address: Standing for Media Access Control, a MAC address is a hardware identifier unique to each network interface card (NIC). It functions at a lower level than IP addresses, operating within the framework of local area networks (LANs). MAC addresses are used for physical device identification, network adapters, and facilitate communication within a local network segment.
5. Destination Address in Different Network Topologies
LANs, WANs, and the Internet
- LANs (Local Area Networks): In LANs, destination addresses are used to direct data to specific devices within a small geographic area, like an office or home. IP and MAC addresses play crucial roles in these local networks.
- WANs (Wide Area Networks): In WANs, which span larger geographic areas, destination addresses ensure data reaches the correct network across cities or countries. WANs often rely on more complex routing protocols and IP address management.
- The Internet: The global network of networks, the Internet uses destination addresses to direct data across diverse paths and multiple networks, ensuring global connectivity.
Role in Network Segmentation and VPNs
- Network Segmentation: Destination addresses are vital in network segmentation, where networks are divided into subnetworks. They help in routing traffic efficiently within and between these segments, enhancing performance and security.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): In VPNs, destination addresses enable secure, encrypted connections over the internet. They guide data to the correct endpoint within a VPN, ensuring that remote users can access network resources securely.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing Conflicts
- IP Address Conflicts: These occur when two devices on the same network are assigned the same IP address. Resolving these conflicts often involves reconfiguring IP settings or implementing a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) system.
- MAC Address Duplication: Rare but problematic, MAC address duplication can disrupt network operations. This issue can be resolved by replacing or reconfiguring the affected hardware.
Routing Errors
- Incorrect Routing: This happens when data packets are misdirected due to incorrect destination addresses or misconfigured routing tables. Troubleshooting involves checking and correcting router configurations and ensuring accurate address assignments.
- Looping: In looping, data packets get stuck in an endless cycle between routers. Resolving this requires modifying routing protocols and sometimes updating network infrastructure.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding destination addresses in various network topologies and their role in efficient data transmission is essential for anyone involved in network design or management. From ensuring data reaches the right device in a LAN to facilitating global communications via the internet, destination addresses are the linchpins of network connectivity. Finally, effective troubleshooting of common issues like address conflicts and routing errors further underscores their importance in maintaining a smooth, functional network.
8. References
- “Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach” by James Kurose and Keith Ross: Provides comprehensive coverage of networking concepts, including IP addressing and network topologies.
- “TCP/IP Illustrated” by W. Richard Stevens: Offers detailed insights into TCP/IP protocols and network communication.
- “Network Warrior” by Gary A. Donahue: A practical guide to network management, covering topics from basic configurations to advanced networking concepts.
See also: IP Address