In an age where digital communication forms the backbone of our interconnected world, understanding digital transmission becomes crucial. Digital transmission, the process of sending information using digital or binary signals, is at the core of virtually all modern communication and data exchange systems.
This article aims to demystify the concept of digital transmission, exploring its mechanics, types, and the crucial role it plays in contemporary networking and communication technologies. Ideal for college students, educators, system administrators, and computer science professionals, this piece provides a comprehensive overview of what digital transmission is and why it’s pivotal in today’s digital era.
In this article:
- What is Digital Transmission?
- Types of Digital Transmission
- Digital Transmission Techniques
- Digital Transmission in Networking
- Challenges and Advancements
- Digital Transmission and Cybersecurity
- Video
- Conclusion
- References

1. What is Digital Transmission?
Digital transmission refers to the process of transferring data in the form of digital signals – a series of binary bits (0s and 1s) – over a communication channel. Unlike analog transmission, which sends data as a continuous signal, digital transmission encodes data into discrete signals, offering a more efficient and reliable means of communication. This method is fundamental to most modern communication and information systems, including the Internet, cellular networks, and digital broadcasting.
With copper cabling, the variable quantity is typically the voltage or the electrical potential. With fiber-optic cabling or wireless communication, variation in intensity or some other physical quantity is used.
Digital signals use discrete values for the transmission of binary information over a communication medium such as a network cable or a telecommunications link. On a serial transmission line, a digital signal is transmitted 1 bit at a time.
Basic Principles
The basic principles of digital transmission involve:
Data Encoding: Information, whether text, voice, or video, is converted into binary format for transmission.
Signal Transmission: These binary signals are then transmitted over a communication channel, such as a wire, fiber optic cable, or even wireless mediums.
Error Detection and Correction: Digital transmission often includes mechanisms for detecting and correcting errors that may occur during transmission.
Differentiating from Analog Transmission
The opposite of digital transmission is analog transmission, in which information is transmitted as a continuously varying quantity. An analog signal might be converted to a digital signal using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and vice versa using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). ADCs use a method called “quantization” to convert a varying AC voltage to a stepped digital one.
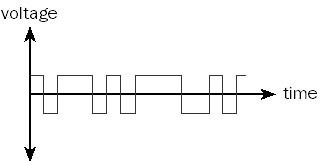
- Signal Type: While analog transmission sends data as continuous waveforms, digital transmission sends data in discrete pulses.
- Error Handling: Digital transmission allows for more precise error detection and correction, enhancing data integrity.
- Capacity and Efficiency: Digital signals can carry more data at higher speeds and are generally more efficient than analog signals.
2. Types of Digital Transmission
Various Types
The primary types of digital transmission include:
- Serial Transmission:
- Description: Data bits are sent sequentially over a single channel. (learn more)
- Pros: Simplified cabling and lower cost; ideal for long-distance transmission.
- Cons: Can be slower than parallel transmission due to sequential bit transfer.
- Parallel Transmission:
- Description: Multiple bits are sent simultaneously over multiple channels (learn more).
- Pros: Higher data transfer rates; suitable for short-distance communication.
- Cons: More complex cabling and higher costs; risk of signal skew.
Pros and Cons of Different Scenarios
- Serial Transmission:
- Best for: Long-distance communication such as data transfer over networks or between computers and peripherals.
- Limitations: Not ideal for scenarios requiring extremely high-speed data transfer over short distances.
- Parallel Transmission:
- Best for: Short-distance, high-speed data transfer requirements, such as within a computer system.
- Limitations: Not practical for long-distance communication due to cable complexity and signal degradation issues.
In summary, the choice between serial and parallel digital transmission depends on factors like distance, speed requirements, and cost considerations. Understanding these types is crucial for professionals designing or managing digital communication systems.
3. Digital Transmission Techniques
Different Techniques
Digital transmission employs various techniques to effectively send data over a network or communication channel:
- Modulation: This technique involves altering a carrier signal to transmit data. In digital transmission, modulation converts digital signals into a form suitable for the transmission medium. Types of digital modulation include Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), and Phase Shift Keying (PSK).
- Multiplexing: Multiplexing allows multiple digital or analog signals to be combined and transmitted over a single channel. The two primary types are Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM).
Practical Applications
- Modulation in Wireless Communications: Digital modulation techniques are widely used in cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and satellite communications to efficiently utilize bandwidth and reduce interference.
- Multiplexing in Telecommunications: TDM is commonly used in digital telephony and data communication networks to maximize the capacity of communication links.
4. Digital Transmission in Networking
Role in Computer Networking
Digital transmission is fundamental in the field of computer networking:
- Data Transfer Mechanism: It serves as the primary mechanism for transferring data across different types of networks, including LANs (Local Area Networks) and WANs (Wide Area Networks).
- Support for Various Network Topologies: Digital transmission adapts to various network topologies and types, such as Ethernet, fiber optic, and wireless networks.
Facilitation of Data Exchange
- Efficient Data Exchange: Digital transmission enables efficient data exchange by using advanced encoding and error-checking techniques, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
- High-Speed Communication: With the advent of technologies like broadband and optical fiber, digital transmission supports high-speed Internet and network communications.
- Versatility: It supports a range of data types (text, audio, video, etc.) and services (voice over IP, streaming, etc.), making it versatile for various networking applications.
Digital transmission techniques like modulation and multiplexing have revolutionized the way data is sent and received in networks. The utilization of these techniques in computer networking has not only enhanced the efficiency of data exchange but also expanded the capabilities of network systems to support a wide array of applications and services.
5. Challenges and Advancements
Current Challenges
Despite its advancements, digital transmission faces several challenges:
- Bandwidth Limitations: As demand for data and speed increases, the bandwidth limitation of existing infrastructure becomes a significant challenge.
- Signal Interference and Attenuation: In wireless transmission, signal interference and attenuation can affect data integrity and transmission quality.
- Scalability Issues: Scaling digital transmission systems to accommodate growing data needs while maintaining efficiency and reliability is a complex task.
Emerging Trends and Future Developments
The field of digital transmission is evolving rapidly, with several trends shaping its future:
- 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G promises higher speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity for digital transmission.
- Quantum Communications: This emerging field could revolutionize digital transmission with potentially unbreakable encryption and ultra-fast speeds.
- Fiber Optic Advancements: Continuous improvements in fiber optic technology are increasing transmission speeds and reducing latency in wired networks.
6. Digital Transmission and Cybersecurity
Relationship with Cybersecurity
Digital transmission and cybersecurity are intrinsically linked:
- Data Integrity and Confidentiality: Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data during digital transmission is a core aspect of cybersecurity.
- Vulnerability to Cyber Attacks: Digital transmission systems can be vulnerable to various types of cyberattacks, making security measures crucial.
Importance of Secure Digital Transmission
- Encryption: Utilizing strong encryption methods is essential for protecting data during transmission.
- Secure Protocols: Implementing secure communication protocols can help safeguard data against interception and unauthorized access.
7. Video: Digital Transmission on YouTube
8. Conclusion
Digital transmission is a cornerstone of modern communication, enabling the rapid and efficient exchange of data in our interconnected world. While it faces challenges like bandwidth limitations and cybersecurity threats, advancements in technology continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in digital communication.
The future of digital transmission looks promising, with emerging technologies poised to offer even faster, more secure, and more efficient methods of data exchange.
9. References
- “Data Communications and Networking” by Behrouz A. Forouzan.
- “Digital Communications” by John G. Proakis.
- “Cybersecurity: The Essential Body of Knowledge” by Dan Shoemaker and Wm. Arthur Conklin.
- RFC 5246 – The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol Version 1.2.