H.323 is a set of protocols that paved the way for voice and video communication over the Internet. Often regarded as the backbone of many legacy VoIP (Voice over IP) and conferencing systems, this protocol suite may seem antiquated but still holds relevance in today’s digital landscape. In this article, we’ll unravel what H.323 is, its historical significance, how it compares to newer protocols like SIP, and why it’s still important to understand it.
Jump to:
- Introduction
- What is H.323
- Historical Context
- Core Components of H.323
- H.323 vs. SIP
- Use Cases
- Security Considerations
- Future Outlook
- Conclusion
- Video: H.323 Gateway Configuration
1. Introduction
What is H.323?
H.323 is a protocol suite approved by the ITU-T, the International Telecommunication Union’s Telecommunication Standardization Sector. It was one of the first protocols designed to facilitate voice and video conferencing over IP networks. The suite is composed of various elements including endpoints, gatekeepers, and gateways, each serving specific functions to enable seamless communication.
Historical Context
The protocol was ratified in 1996 at a time when the Internet was still nascent, and real-time communication technologies were in their infancy. Back then, most voice and video communication occurred over circuit-switched networks, which were both inefficient and costly. H.323 emerged as a groundbreaking solution that leveraged the capabilities of IP networks, thus providing a more efficient and flexible alternative for real-time multimedia communications.
In its heyday, H.323 was the de facto standard for Internet telephony and video conferencing, before newer protocols like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) came into the picture. Despite its declining popularity in favor of more modern solutions, H.323 remains in use in various legacy systems around the world.
By understanding H.323’s origins and fundamental components, you gain not only a historical perspective but also insights into the evolution of voice and video conferencing technologies. As we delve deeper into the workings and nuances of H.323 in subsequent chapters, you’ll see why this protocol suite remains an important subject in the realm of IP-based communications.
ITU-T H.323 Recommendation Summary
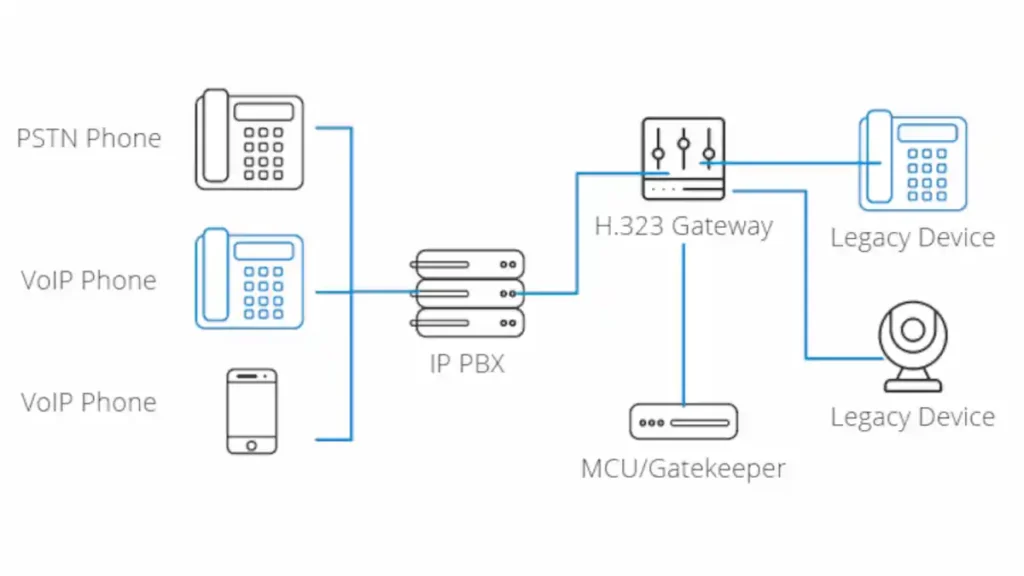
2. Core Components of H.323
Understanding H.323 requires an in-depth look at its core components—endpoints, gatekeepers, gateways, and MCUs (Multipoint Control Units). Each plays a specific role in establishing and managing real-time multimedia communication over IP networks.
Endpoints
Endpoints are the actual devices or software applications that users directly interact with during a call. This includes IP phones, video conferencing units, and softphones running on computers or mobile devices.
Endpoints are critical because they initiate and terminate the actual communication, whether it’s a voice call, video conference, or data sharing session. They also implement various H.323 protocols to ensure seamless interaction and high-quality multimedia transmission.
Gatekeepers
Gatekeepers serve as the central management unit in an H.323 environment. They are responsible for addressing, authentication, and call routing.
In large networks, the role of a gatekeeper is vital for effective resource management and security. By centralizing the control of calls, a gatekeeper minimizes latency and optimizes bandwidth usage while ensuring only authorized users access the network.
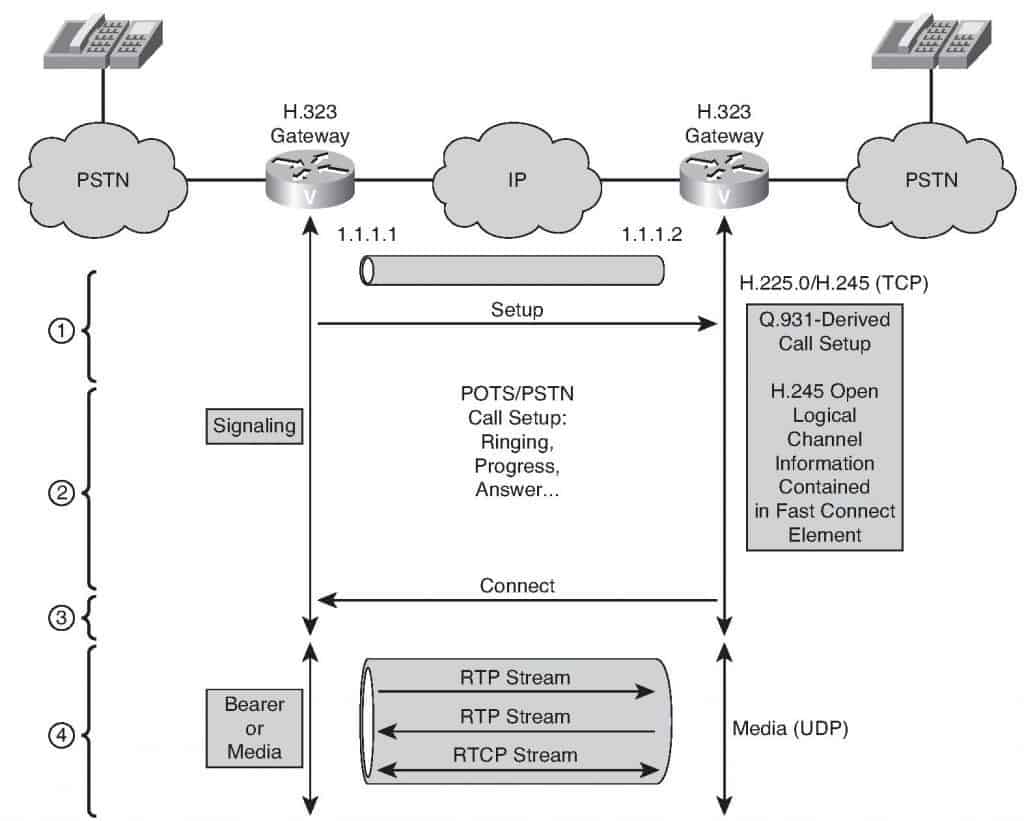
Gateways
Gateways function as translators between different network protocols. They allow H.323 endpoints to communicate with devices using other protocols like SIP or PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network).
Gateways extend the flexibility and utility of H.323 environments by providing interconnectivity with other communication systems. This is particularly useful for businesses operating both legacy and modern communication solutions.
MCUs (Multipoint Control Units)
MCUs manage multiparty conferences by coordinating the mixing, switching, and splitting of media streams.
In video conferencing scenarios involving multiple participants, an MCU plays a crucial role. It ensures that all endpoints can communicate with each other efficiently, regardless of the number of participants or the types of media being shared.
Each of these core components plays an indispensable role in the functionality and efficiency of an H.323 network. As we delve into later chapters comparing H.323 with contemporary protocols and discussing its current relevance, the significance of these building blocks will become increasingly clear. Understanding them lays the foundation for grasping the broader complexities and capabilities of H.323 as a pioneering protocol suite for multimedia communication.
3. H.323 vs. SIP
When discussing real-time multimedia communication over IP, two protocols often emerge as the focal point of the conversation: H.323 and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). Though both serve similar purposes—facilitating voice, video, and data communications—they differ fundamentally in architecture, flexibility, and implementation. Understanding these differences is key for anyone grappling with the evolution of IP-based communications.
Architectural Complexity
- H.323 is often viewed as more complex due to its collection of elements like endpoints, gatekeepers, gateways, and MCUs, each performing distinct roles in the network.
- SIP: In contrast, SIP opts for a more streamlined architecture. With its focus on endpoint-to-endpoint communications, SIP often bypasses the need for a central coordinating unit like a gatekeeper, making the setup simpler but potentially less controlled.
Flexibility and Extensibility
- H.323 was designed with a tightly-coupled architecture, resulting in less flexibility when it comes to adding new features or integrating with other protocols.
- SIP is more modular and extensible, allowing easier integration of new functionalities and compatibility with various web services. This makes SIP a more attractive option for networks that require adaptability.
Protocol Suitability
- H.323 was initially intended for multimedia communication and thus has a rich feature set for video conferencing, making it a go-to choice for legacy systems with complex conferencing needs.
- SIP, while capable of supporting video and data, was primarily designed for voice communication. As a result, it is often the protocol of choice for straightforward VoIP services.
Security Measures
- Security in an H.323 network can be quite robust, especially with a central gatekeeper managing authentication and authorization. However, the complexity of the protocol suite can make it challenging to secure effectively.
- SIP generally offers more straightforward security mechanisms, partly because of its simpler architecture. Implementing features like SIP trunking can also enhance network security.
Call Setup and Management
- H.323 employs a binary-based protocol called Q.931 for call setup, which, although reliable, tends to be slower and more resource-intensive.
- SIP uses a text-based format similar to HTTP for initiating and managing sessions, making it easier to debug and integrate with web-based applications.
As technologies evolve, the debate over H.323 vs. SIP will continue to shift. However, understanding their core differences and respective strengths and weaknesses is crucial for anyone working in the field of IP-based communications. Whether you’re managing a legacy system or deploying a modern network, knowledge of both protocols will equip you with the tools to make informed decisions.
4. Use Cases
H.323 may seem like a relic of the past, but it retains relevance in specific scenarios and environments. In this chapter, we’ll explore use-cases where this set of protocols still holds its ground.
Legacy Systems
Many businesses continue to operate older communication systems where migrating to a newer protocol would be costly and time-consuming. H.323’s robust feature set ensures that these legacy systems continue to provide value.
Specialized Industry Applications
Industries like healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing sometimes use proprietary hardware that is optimized for this set of protocols. Switching to a different protocol might not offer any significant advantages and could introduce compatibility issues.
Large-Scale Video Conferencing
In situations requiring complex video conferencing setups involving multiple parties and different types of media, H.323, with its support for MCUs, often excels.
Global Operations
For companies with offices around the world, including locations with limited technological infrastructure, H.323 offers a stable and universally supported protocol.
Interoperability
In mixed environments where various protocols must co-exist, the H.323 gateway provides an effective bridge to ensure smooth communication.
5. Security Considerations
Security remains a paramount concern in any communication setup, and H.323 is no exception. In this chapter, we’ll delve into the security features, as well as limitations, of H.323.
Authentication and Authorization
A central gatekeeper in an H.323 network manages user authentication and authorization, ensuring only approved devices and users can access the system. However, this centralized model may pose a single point of failure if compromised.
Data Encryption
H.323 supports various encryption methods to secure data transmission. Nevertheless, the implementation of these methods can sometimes be cumbersome, owing to the protocol’s inherent complexity.
Vulnerabilities
Like any other protocol, H.323 has its vulnerabilities, such as susceptibility to Denial of Service (DoS) attacks or unauthorized access through poorly secured endpoints.
Firewall and NAT Traversal
One notable limitation is that H.323 can struggle with traversing firewalls and Network Address Translation (NAT) setups. Special configurations are often required to ensure seamless communication, which could compromise security if improperly configured.
Best Practices
To mitigate these risks, employing intrusion detection systems, regular security audits, and robust encryption are advised. The gatekeeper’s settings should be configured to enforce strong authentication and authorization policies.
6. Future Outlook
So, what does the future hold for H.323?
Continued Relevance in Legacy Systems
Firstly, one thing remains clear: H.323 isn’t going anywhere anytime soon, especially when it comes to legacy systems. These older setups continue to rely on H.323’s robust feature set, and for many organizations, the cost and effort associated with migrating to newer protocols are not justified by the potential benefits.
Integration Challenges
On the flip side, integration with more modern, cloud-based services can pose a challenge for H.323 systems. As newer protocols like SIP gain widespread adoption, the risk of H.323 becoming more isolated increases.
Niche Applications
Nevertheless, H.323 continues to find niche applications where its particular strengths—such as interoperability through gateways and robust video conferencing features—prove invaluable. In specialized industries like healthcare and manufacturing, for instance, the protocol can meet specific requirements that newer protocols can’t address as effectively.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Moreover, there’s potential for H.323 to adapt and integrate machine learning algorithms and AI for enhanced functionality and security. Although this is still largely theoretical, such integration could breathe new life into the protocol.
Convergence and Hybrid Solutions
Finally, as networks become more complex, the future might see a convergence of various protocols, including H.323, into hybrid solutions. These would leverage the strengths of multiple protocols to deliver more flexible and robust communication systems.
In summary, while H.323 might not be the go-to option for new system deployments, its relevance should not be underestimated. Whether it evolves to integrate newer technologies or remains a stable choice for specific applications, H.323 will likely continue to play a role in the world of IP-based communications for years to come.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, as we reflect on the intricacies of H.323, it becomes evident that a comprehensive understanding of this protocol remains crucial, especially for those dealing with legacy systems. H.323 Explained isn’t just about digging up a historical artifact; it’s about appreciating a foundational technology that still has real-world applications today.
As a next step, consider conducting a security audit of your H.323 network components, from endpoints to gatekeepers and particularly the gateways. For newcomers, delving into additional educational resources can provide a deeper understanding of how H.323 operates. As for veterans, revisiting and potentially updating your H.323 configurations can offer a critical security refresh.
H.323 Explained offers more than just a technical overview; it provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of a protocol that continues to operate at the intersection of technology’s past and future.
By closing this knowledge gap, you’ll not only better secure your communications but also gain a broader perspective on the development of real-time multimedia communications. After all, understanding where we’ve been is instrumental in shaping where we’re headed.
So, as you transition to what’s next—whether that’s updating your H.323 system or migrating to a newer protocol—carry with you the insights and knowledge gleaned from this deep dive into this technology.
8. H.323 Gateway Configuration
Video training for Cisco Certification programs: CCNA, CCNP and CCIE.