At the close of the 20th century, Microsoft introduced an innovative feature to its Windows 98 and Windows 2000 operating systems: the Accessibility Wizard. This utility, designed with a clear purpose, sought to configure computers specifically for individuals with impaired visual or motor skills, bridging a technological gap for many users. While the term “Accessibility Wizard” might not ring a bell for many younger users today, its impact is undeniable.
This article delves into the evolution of Microsoft’s accessibility features, tracing its journey from the inception of the Accessibility Wizard to the advanced and integrated tools found in today’s Windows OS.
In this article:
- What was the Accessibility Wizard
- The Imperative of Accessibility in Technology
- The Move to Built-in Accessibility: Windows XP and Vista
- Enhanced Integration: Windows 7 to Windows 10
- The Modern Era: Windows 11 and Beyond
1. What was the Accessibility Wizard
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, Microsoft introduced the “Accessibility Wizard” to the Windows operating system, starting with Windows 98 and continuing with Windows 2000. This tool was a revolutionary step forward, aiming to make computers more accessible to individuals with different abilities.
The Accessibility Wizard was a utility specifically designed to guide users through a series of questions, allowing them to tailor their PC’s settings to their needs. Whether someone had impaired vision, hearing, or motor skills, the wizard would adjust the computer’s settings to accommodate these specific requirements. This could include magnifying screen content, adjusting colors, or setting up StickyKeys for users who had difficulty pressing multiple keys at once.
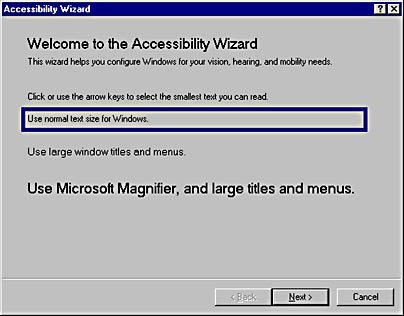
How it worked
To start the Accessibility Wizard, choose Accessories from the Start menu. Then from the Accessibility program group, choose Accessibility Wizard. Note that in Windows 98, you might have to install the Accessibility Tools to gain access to the wizard.
The wizard leads the user through a series of questions concerning his or her disability and configures mouse, keyboard, and display properties to meet the particular need.
This tool gives administrators the ability to configure workstations for individuals with physical impairments by leading the user through a series of screens that he or she can then respond to in real-time.
Using the Accessibility Wizard is generally more convenient than using the Accessibility Options property sheet to configure accessibility settings. The wizard’s final screen lists the accessibility options that have been enabled.
2. The Imperative of Accessibility in Technology
Accessibility isn’t just a buzzword in the realm of technology—it’s a fundamental necessity. The digital age has brought with it unprecedented opportunities, from information access to communication tools to entertainment platforms. Yet, if these opportunities aren’t accessible to everyone, regardless of their physical abilities, then we risk creating a divide that excludes a significant portion of the population.
The significance of features like the Accessibility Wizard and its successors is multifold:
- Inclusion and Empowerment: Accessibility features empower individuals with disabilities by providing them with tools to operate computers and access information independently. This autonomy can lead to increased confidence and a sense of inclusion in the digital community.
- Economic Opportunities: As many job roles and opportunities move online, having accessible tools ensures that individuals with disabilities aren’t left behind. They can actively participate in the workforce, contribute to the economy, and achieve their professional goals.
- Education: The realm of education has dramatically transformed with digital tools, online courses, and e-learning platforms. Ensuring these tools are accessible allows every student, irrespective of their physical abilities, to benefit from educational advancements.
- Social Integration: With social networks and communication tools becoming primary means of staying connected, accessibility ensures everyone can communicate, socialize, and be a part of global conversations.
- Fostering Innovation: Designing for accessibility often pushes tech companies to think outside the box, leading to innovative solutions that can benefit all users, not just those with disabilities.
In essence, accessibility in technology isn’t just about adapting tools for a subset of users; it’s about expanding the horizons of what’s possible and ensuring everyone has a seat at the digital table. By ensuring computers and software are designed with everyone in mind, we create a more inclusive, diverse, and forward-thinking digital landscape.
3. The Move to Built-in Accessibility: Windows XP and Vista
As the Windows OS evolved, so did its accessibility features. With Windows XP and later with Windows Vista, the accessibility settings became more integrated into the system. The Accessibility Wizard was replaced by the Ease of Access Center. This tool wasn’t just a setup guide anymore; it became a central hub where users could explore and adjust a myriad of settings to fit their needs.
» To read next: Demystifying ClearType!
4. Enhanced Integration: Windows 7 to Windows 10
The journey continued with Windows 7, 8, and 10. Microsoft steadily improved upon its accessibility offerings, adding more sophisticated tools and a broader range of settings. The “Ease of Access” settings in these versions provided tools such as the Magnifier, Narrator, and On-Screen Keyboard. High contrast themes became more refined, catering to those with visual impairments.
With the introduction of touchscreens and digital pens, Windows also incorporated features like Windows Ink, allowing users to interact with their devices in novel ways that could be beneficial for those with specific motor skill challenges.
See also: Accessibility Options: technology to all individuals.
5. The Modern Era: Windows 11 and Beyond
The release of Windows 11 saw a further integration of accessibility features. No longer relegated to a specific section, these tools permeated every aspect of the OS. New features, such as enhanced voice typing and improved eye-tracking controls, made the Windows experience even more inclusive.
Connecting the Past to the Present
While the specific “Accessibility Wizard” may have faded into the annals of tech history, its legacy is apparent in every corner of modern Windows versions. What began as a simple utility has grown into a comprehensive suite of tools that emphasizes Microsoft’s commitment to making computing accessible to everyone.
Today, users don’t need a separate wizard because accessibility is ingrained in the very fabric of Windows. It’s a testament to how far technology has come in ensuring that everyone, regardless of their physical abilities, can have a seamless and enriching computing experience.
See also: Microsoft Commitment to Accessibility