AppleTalk, a pioneering force in the realm of networking, stands as the foundational protocol that powered early Apple networks. Launched in 1985, it was instrumental in enabling Apple devices to seamlessly communicate with each other, sharing resources such as files and printers with remarkable ease.
AppleTalk’s significance extends beyond its technical capabilities; it marked a pivotal moment in networking history, shaping the way devices interacted within the Apple ecosystem. As technology advanced, AppleTalk evolved, paving the way for more modern network protocols.
This article delves into the intricacies of AppleTalk, exploring its architecture, functionalities, and the crucial role it played in the networking world.
Table of Contents:
- Overview of AppleTalk
- Historical Development and Adoption
- AppleTalk in Network Infrastructure
- Transition to Apple Open Transport
- Legacy and Modern Relevance
- References
1. Overview of AppleTalk
Basic Architecture and Features
AppleTalk was designed with simplicity and efficiency in mind, catering to the needs of small-scale networks. Its architecture comprised several key components:
- Network Layer Protocol: AppleTalk’s network layer protocol facilitated data packet routing between devices, ensuring efficient communication across the network.
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): A critical part of AppleTalk, ARP managed the mapping of network addresses to physical hardware addresses, crucial for data transmission.
- AppleTalk Filing Protocol (AFP): AFP allowed file sharing across the network, enabling users to access and modify files stored on different machines.
- Printer Access Protocol (PAP): PAP provided the means for networked printer sharing, a significant feature in office settings.
Facilitating Network Communication
AppleTalk’s significance in early Apple networks was marked by its user-friendly approach to networking. It offered:
- Plug-and-Play Connectivity: AppleTalk allowed devices to connect to the network with minimal configuration, making network setup and expansion straightforward.
- Automatic Address Assignment: The protocol dynamically assigned addresses to devices on the network, eliminating the need for manual configuration.
- Inter-Device Communication: By standardizing the way Apple devices communicated, AppleTalk laid the groundwork for a cohesive network environment where resource sharing was seamless and intuitive.
In essence, AppleTalk was not just a technology; it was a gateway that opened up new possibilities in the realm of network communication for Apple users. Its architecture and features were thoughtfully crafted to create an interconnected network that was accessible, efficient, and robust.
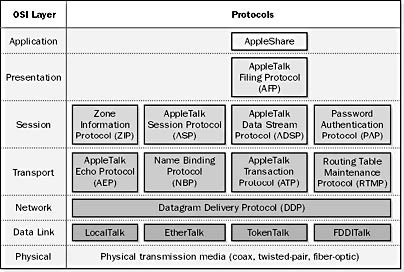
AppleTalk by layer (OSI Model)
AppleTalk is a suite of networking protocols that work together to provide file and print sharing services to Macintosh networks. The following illustration shows the details of the AppleTalk protocol suite and its relationship with the seven-layers OSI model.
Note:
Apple Open Transport includes an updated version of AppleTalk with additional features such as support for manually assigned node addresses, support for multihomed and multinode systems, and other features.
2. Historical Development and Adoption
Origins and Early Adoption
AppleTalk’s journey began in 1985, a period marked by the burgeoning growth of personal computing. Developed by Apple Inc., it was introduced as an integral part of the Apple Macintosh line. Designed for simplicity and user-friendliness, AppleTalk rapidly became a staple in the Apple ecosystem.
- Impact in the 1980s and 90s: During these decades, AppleTalk played a pivotal role in establishing networked environments in homes and offices. Its ease of use and reliability made it a preferred choice for Apple users, fostering a networked culture that was previously complex and inaccessible to the average user.
- Facilitating Small Network Setups: AppleTalk’s architecture was ideally suited for small to medium-sized networks, making it popular in educational institutions and small businesses.
Cross-Platform Availability
AppleTalk’s influence extended beyond the Apple ecosystem, demonstrating its versatility and broad appeal.
- IBM PC and Compatibles: Recognizing the need for cross-platform compatibility, versions of AppleTalk were developed for IBM PCs and compatible systems. This move facilitated communication between Apple and non-Apple devices, breaking down barriers in network interoperability.
- Apple IIGS Integration: The Apple IIGS, with its advanced graphics and sound capabilities, also leveraged AppleTalk. This integration allowed for a more cohesive and versatile use of Apple’s range of computing products.
3. AppleTalk in Network Infrastructure
Integration into Printers, File Servers, and Routers
AppleTalk’s architecture was not limited to personal computers; it extended its reach into various network devices.
- Printers: One of AppleTalk’s standout features was its ability to network printers. This functionality allowed multiple users on the same network to access and use a single printer, streamlining resource sharing in office environments.
- File Servers: AppleTalk played a crucial role in file server connectivity. It enabled servers to communicate efficiently with Apple devices, facilitating file storage and sharing across the network.
- Routers: The protocol was also integrated into routers, where it managed the routing of data packets across different network segments, enhancing connectivity and data flow.
Networking Capabilities
The integration of AppleTalk into these devices significantly enhanced network capabilities:
- Simplified Device Communication: AppleTalk’s plug-and-play nature simplified the process of adding devices to a network. This ease of integration was a hallmark of AppleTalk’s design philosophy.
- Efficient Resource Management: The protocol’s ability to manage resources like printers and file servers effectively made it an asset in network management, particularly in multi-device environments.
In summary, AppleTalk’s historical development and adoption marked a significant era in personal computing and networking. Its integration into various network infrastructure components further solidified its status as a versatile and efficient networking solution. The protocol’s ability to bridge different platforms and devices underscored its innovative and forward-thinking design, leaving a lasting legacy in the world of networking.
4. Transition to Apple Open Transport
The Shift from AppleTalk
The evolution of networking technologies in the mid-1990s prompted a significant shift from AppleTalk to a more advanced and versatile framework known as Apple Open Transport. This transition marked a new era in Apple’s networking strategy.
- Integration of Advanced Protocols: Apple Open Transport was introduced to provide a more robust and flexible networking environment. It was designed to support a wider range of network protocols, including the increasingly popular TCP/IP, which was fundamental for internet connectivity.
- Enhanced Network Capabilities: This transition enabled Apple devices to better integrate into diverse network environments, particularly those dominated by the emerging global internet infrastructure.
Expansion to Include TCP/IP
- Broader Connectivity: Apple Open Transport’s support for TCP/IP opened up a world of possibilities for Apple users, allowing seamless interaction with the burgeoning internet and compatibility with a multitude of network architectures.
- Versatility: The addition of TCP/IP and other protocols under the Apple Open Transport umbrella represented a significant step towards interoperability and versatility in network communications for Apple devices.
5. Legacy and Modern Relevance
Reflecting on AppleTalk’s Legacy
AppleTalk’s impact on networking is both profound and enduring. It laid the groundwork for user-friendly network communication and influenced the development of future networking solutions.
- Foundation for Future Technologies: The principles and innovations introduced by AppleTalk, such as ease of use and network integration, have been instrumental in shaping modern networking technologies.
- Influence on Networking Protocols: AppleTalk’s design philosophy influenced the development of networking protocols that prioritize user accessibility and seamless network integration.
Relevance in Today’s Technology Landscape
- Historical Significance: Understanding AppleTalk provides valuable insights into the evolution of network protocols and the history of networking technologies.
- Educational Value: For networking professionals and enthusiasts, knowledge of AppleTalk is a window into the challenges and solutions of early network design, offering a foundational perspective on network protocol development.
6. References
- “AppleTalk Network System Overview” by Apple Computer Inc.: A comprehensive guide detailing the architecture and functionalities of AppleTalk.
- “Interconnecting with TCP/IP: Principles, Protocols, and Architectures” by Douglas E. Comer: Provides insights into the TCP/IP protocol suite, with references to AppleTalk’s role in the broader networking context.
- RFC 1742 (AppleTalk Management Information Base II): Details the management information base for AppleTalk, offering technical insights into the protocol’s operation.
- “Networking Essentials” by Jeffrey S. Beasley: Covers fundamental networking concepts, including a historical overview of AppleTalk.
- “Data and Computer Communications” by William Stallings: Offers an in-depth look at various network technologies and protocols, including AppleTalk and its transition to Apple Open Transport.
- AppleTalk Video – Network Encyclopedia YouTube Channel