In an era where digital communications underpin most of our daily interactions, the role of authentication in networking becomes increasingly paramount. Authentication serves as the gatekeeper in the digital world, determining who is allowed access and who is not.
This process is fundamental to securing networks and protecting digital identities from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Understanding what authentication is and how it operates within the networking landscape is essential for anyone involved in managing or securing digital systems. This article aims to unpack the intricacies of authentication, exploring its methods, protocols, and the critical role it plays in maintaining the integrity of networked systems.
In this article:
- What is Authentication in networking?
- Types of Authentication Methods
- The Role of an Authentication Server
- Authentication Protocols and Standards
- Implementing Authentication in Network Security
- Challenges and Future of Authentication in Networking
- Conclusion
- References

1. What is Authentication in networking?
Authentication in networking is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device attempting to access a network. It’s a security measure that ensures only authorized entities can access network resources and data. The process typically involves validating credentials like usernames, passwords, or digital certificates against a database of authorized users.
Differentiation from Other Security Mechanisms
- Authentication vs. Authorization: While authentication is about verifying identity, authorization determines what an authenticated user or device is permitted to do within the network.
- Authentication vs. Encryption: Encryption is about protecting data integrity and privacy by converting data into a coded format. Authentication, on the other hand, is about verifying the identity of those who wish to access the data.
2. Types of Authentication Methods
Exploration of Various Methods
Several authentication methods are employed in networking, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
- Passwords: The most common form of authentication involving a secret word or phrase known only to the user.
- Pros: Simple to implement and use.
- Cons: Vulnerable to theft, guessing, or brute force attacks.
- Biometrics: Involves using unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial recognition for authentication.
- Pros: Extremely difficult to replicate, offering high security.
- Cons: Can be expensive to implement and raises privacy concerns.
- Tokens: Hardware or software-based tokens generate a one-time password or PIN.
- Pros: Adds an extra layer of security as the token is separate from the user’s device.
- Cons: Tokens can be lost or stolen, and hardware tokens incur additional costs.
- Digital Certificates: Employ cryptographic techniques and are used in public key infrastructure (PKI).
- Pros: Provides strong authentication and can also ensure data integrity and encryption.
- Cons: Complex to implement and manage.
- Two-Factor or Multi-Factor Authentication (2FA/MFA): Combines two or more different types of authentication methods.
- Pros: Significantly increases security by adding multiple layers of defense.
- Cons: Can be more complex for users and may require additional hardware or software.
In conclusion, the choice of authentication method depends on a balance between the desired level of security and practical considerations like cost, user convenience, and system complexity. Each method has its place in the network security toolkit, and often, a combination of these methods is used to achieve a robust authentication system.
3. The Role of an Authentication Server
What is an Authentication Server?
An authentication server is a dedicated server used within networks to authenticate user or device credentials before granting access to network resources. It acts as a central authority that validates identities based on stored credentials, ensuring that only authorized entities can access the network.
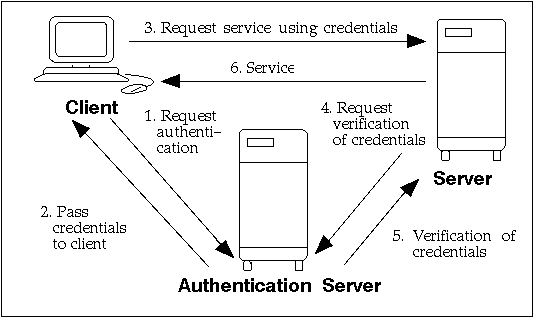
Function in Network Security
The authentication server plays a pivotal role in network security:
- Centralized Authentication Management: It centralizes the management of user credentials and access control, simplifying security administration.
- Verification Process: When a user attempts to access the network, the authentication server verifies the credentials against its database. If the credentials match, access is granted; otherwise, it is denied.
Validation Process of User Credentials
- Credential Submission: The user submits credentials, such as a username and password or digital certificates.
- Credential Verification: The authentication server checks the submitted credentials against its database of authorized users.
- Access Decision: If the credentials are valid, the server permits access to the network; invalid credentials result in access denial.
4. Authentication Protocols and Standards
Common Protocols and Standards
Several authentication protocols and standards are integral to network security:
- Kerberos: A network authentication protocol that uses tickets to allow nodes to prove their identity securely over a non-secure network. (learn more about Kerberos)
- Security Mechanism: It uses strong cryptography to ensure that user credentials are not exposed during transmission.
- RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service): A widely used protocol for remote user authentication and accounting. (learn more about Radius)
- Application: Primarily used by ISPs and enterprises to manage access to internet or intranet resources.
- LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol): Used for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over a network.
- Function: LDAP is often used for storing user credentials and policy information in a central directory.
Ensuring Secure Authentication
- Encrypted Communication: These protocols typically involve encrypted communication, ensuring that credentials are transmitted securely.
- Ticketing and Tokens: Protocols like Kerberos use ticketing mechanisms, offering an added layer of security by minimizing password transmission.
- Centralized Control: With LDAP and RADIUS, administrators can manage and enforce authentication policies centrally, enhancing overall network security.
In summary, authentication servers, supported by robust protocols and standards, are crucial in safeguarding network access and protecting sensitive information. They provide the infrastructure needed to authenticate users effectively and manage access rights, forming the backbone of network security strategies.
5. Implementing Authentication in Network Security
Best Practices for Robust Authentication Systems
To ensure effective authentication in network security, consider these best practices:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add layers of security beyond just passwords. This can include combinations of something the user knows (password), has (token), or is (biometric verification).
- Regularly Update Authentication Protocols: Keep your authentication protocols updated to protect against new vulnerabilities.
- Educate Users: Provide training for users on the importance of strong passwords and how to recognize phishing attempts.
Tips for Network Administrators
- Monitor Authentication Logs: Regularly monitor authentication logs for any unusual activity that might indicate an attempted breach.
- Secure Authentication Servers: Ensure that your authentication servers are secured against attacks and unauthorized access.
- Backup Authentication Data: Regularly backup authentication data to prevent loss in case of system failures.
6. Challenges and Future of Authentication in Networking
Current Challenges
Network authentication faces several challenges:
- Phishing Attacks: Despite robust authentication methods, phishing remains a significant threat, tricking users into revealing credentials.
- Password Management: Managing a large number of passwords securely is increasingly complex.
- Balancing Security and User Convenience: Creating a secure system that is also user-friendly continues to be a challenge.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
- Biometric Authentication: Advancements in biometric technologies offer more secure and convenient authentication methods.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are being explored for detecting and responding to authentication threats more effectively.
- Decentralized Authentication: The use of blockchain and decentralized systems for authentication is an emerging trend that might address some current challenges.
7. Conclusion
Authentication is a fundamental component of network security, acting as the first line of defense in protecting digital resources. The evolution of authentication technologies reflects the ongoing battle between security needs and the ingenuity of cyber threats. As we look to the future, the focus will likely be on developing more sophisticated and user-friendly authentication methods to meet the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity.
8. References
- “Computer Security: Principles and Practice” by William Stallings and Lawrie Brown.
- “Network Security Essentials” by William Stallings.
- RFC 5280 – “Internet X.509 Public Key Infrastructure Certificate and Certificate Revocation List (CRL) Profile”.
- RFC 6749 – “The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework”.