Our Latest Articles
-
Remote Access Service (RAS)
Definition of Remote Access Service (RAS) in Network Encyclopedia. What is Remote Access Service (RAS)? RAS (Remote Access Service) is an optional Microsoft Windows OS Family networking service that provides remote access for remote clients. A machine running Windows on which Remote Access Service (RAS) is installed is called a RAS server. How It Works…
-
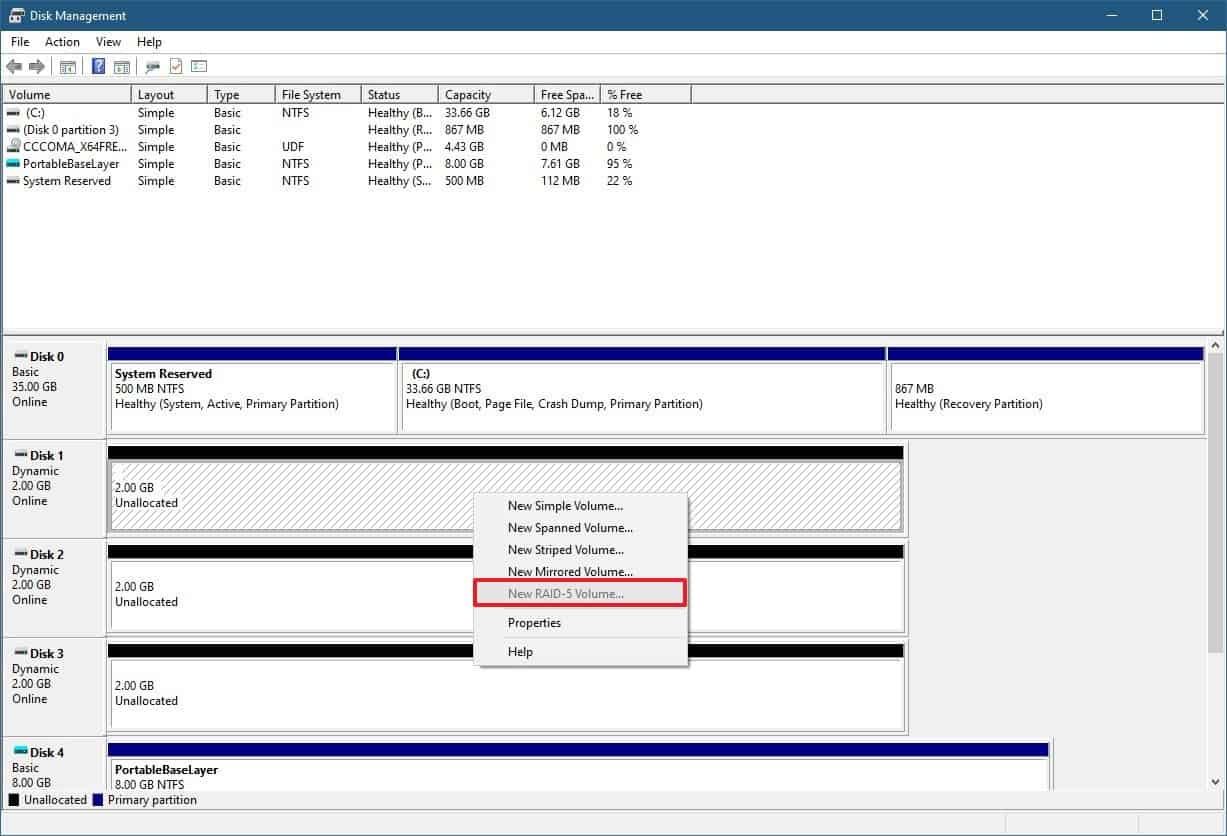
RAID-5 volume
RAID 5 Volume is a volume created with the Disk Management portion of the Computer Management tool that stores its data with parity information across multiple physical disks.
-
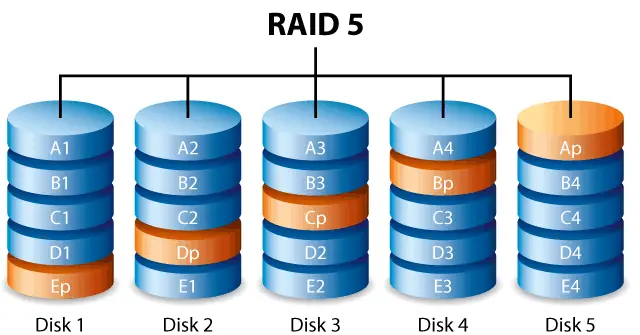
Raid 5 – Implementing disk striping with parity
Guide to help you implement RAID 5 (striping with parity) on Windows Server.
-
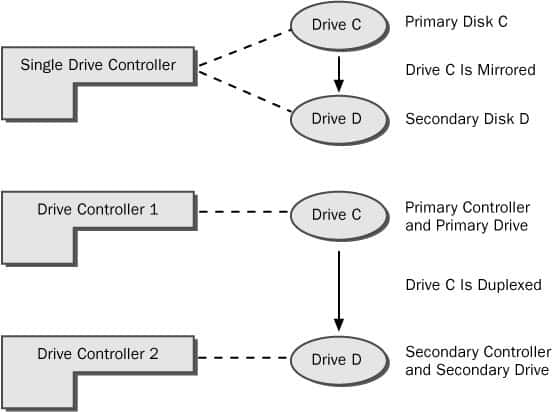
Raid 1 – Implementing Mirror Disk on a server
Guide to help you implement RAID 1 (Mirror Disk) on Windows Server.
-
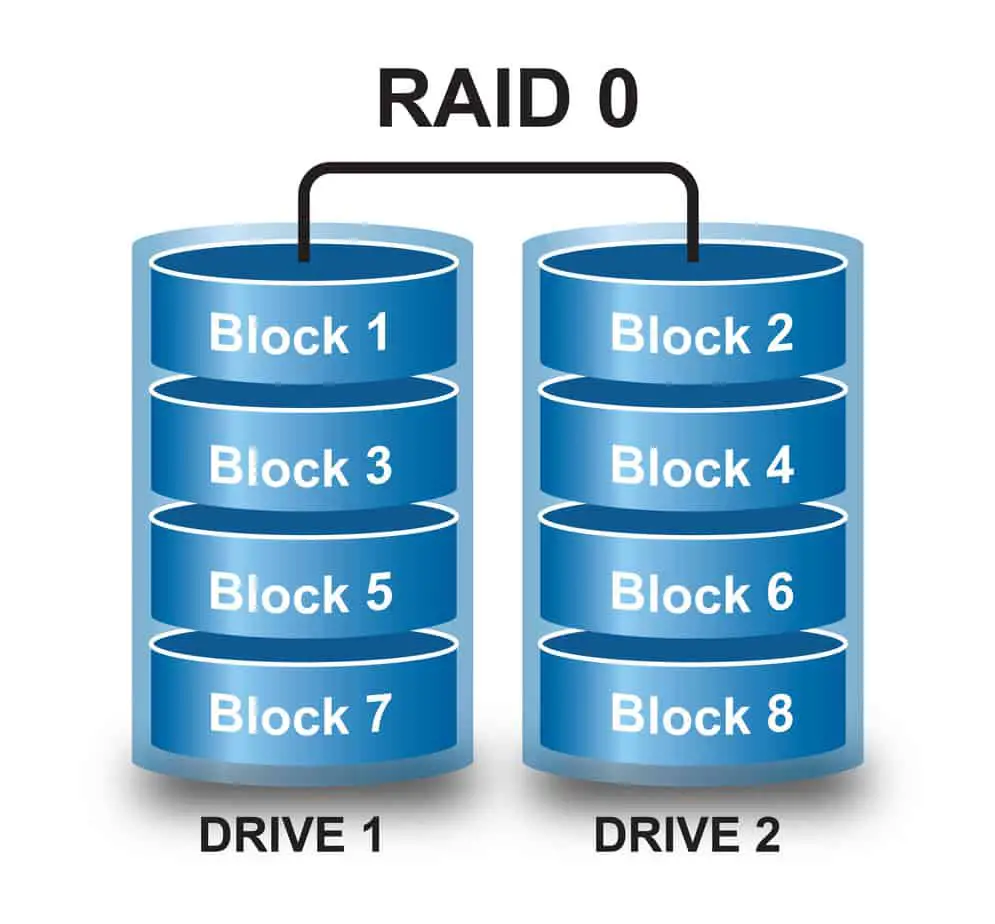
Raid 0 – Implementing disk striping
Guide to help you implementing RAID 0 on Windows Server.
-
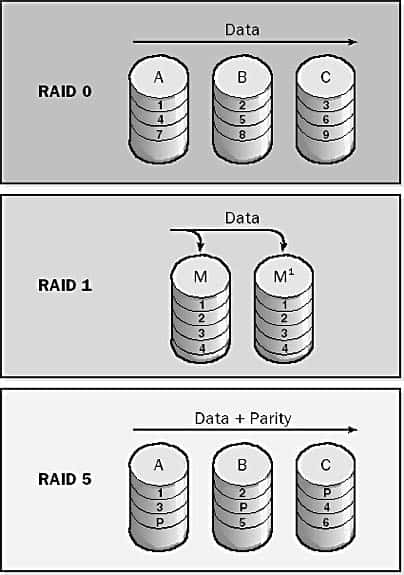
RAID
RAID stands for redundant array of independent disks, is a technology for implementing fault-tolerance on a disk subsystem by using data redundancy, either using software or using a separate hardware RAID storage unit.
-
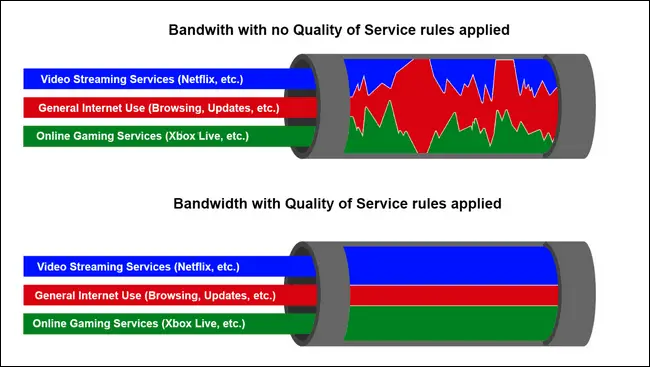
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS is any networking technology that has predictable latency and data loss.
-
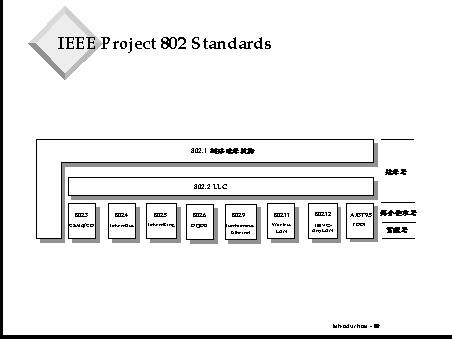
Project 802
Dive into Project 802—an IEEE initiative defining LAN and WAN technologies. Explore its major subsections like 802.1 to 802.14, covering everything from Ethernet to network security.
-
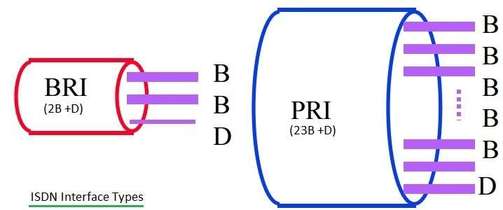
PRI-ISDN: Primary Rate Interface ISDN
Explore the legacy of PRI-ISDN: a once-dominant ISDN framework for digital communication, now overtaken by modern telecommunication technologies.
-

Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC)
Permanent Virtual Circuit is a form of telecommunications service for wide area networks (WANs) that provides a dedicated switched circuit between two nodes in a circuit-switched network.
-

Pass-Through Authentication
Pass-Through Authentication is a method of performing authentication to a domain controller that resides in a trusted domain.
-
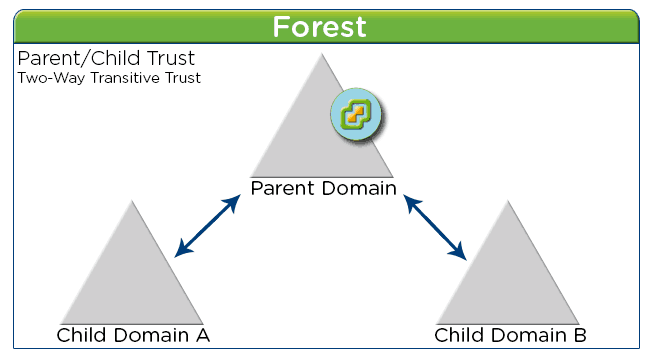
Parent Domain
Parent Domain is a domain in a Microsoft Windows Server domain tree whose Domain Name System (DNS) name forms the basis of subdomains called child domains.