Our Latest Articles
-
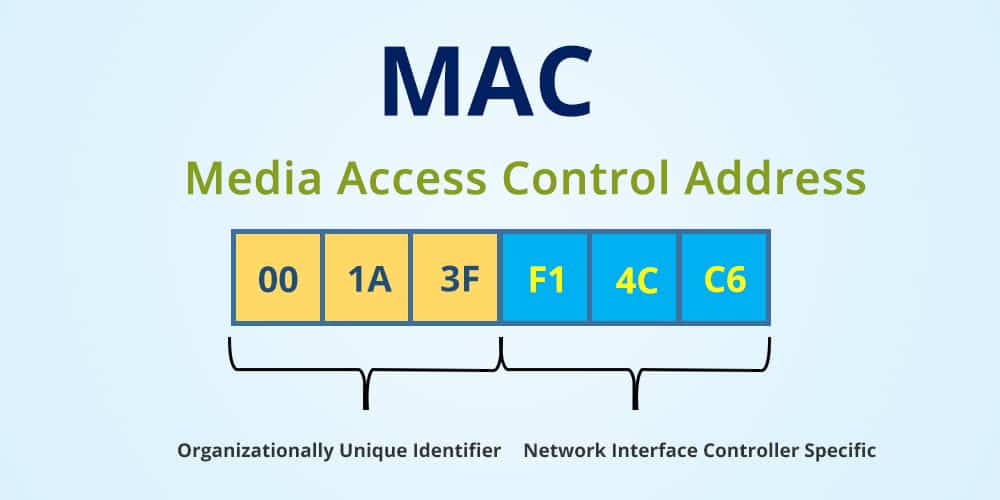
MAC Address
MAC Address is a unique 6-byte (48-bit) address that is usually permanently burned into a network interface card (NIC) or other physical-layer networking device and that uniquely identifies the device on an Ethernet-based network.
-
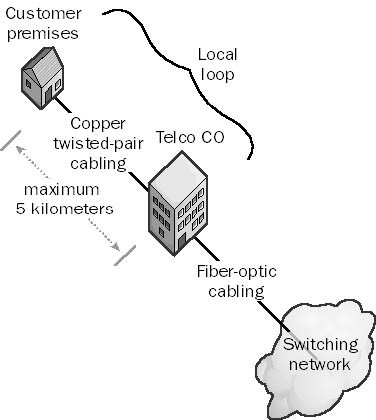
Local Loop
Local Loop is the portion of the telephone system that connects your home or office to the nearest central office (CO) of your local telco.
-
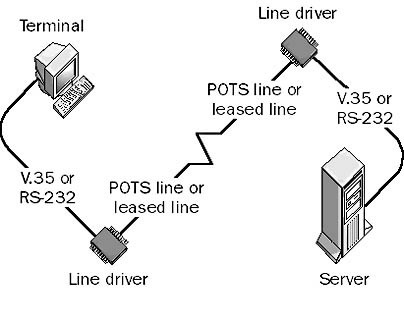
Line Driver
Line Driver is a device that can use installed twisted-pair phone lines or leased lines to connect terminals to servers in different parts of a building or in different buildings.
-

Line Coding
Line Coding is a method of placing digital signals on a wire.
-
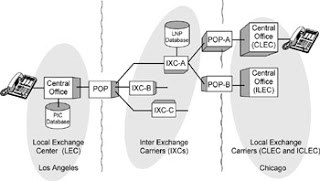
Local Exchange Carrier (LEC)
LEC stands for Local Exchange Carrier, is a telco in the United States that provides local telephone and telecommunication services to businesses and individuals.
-
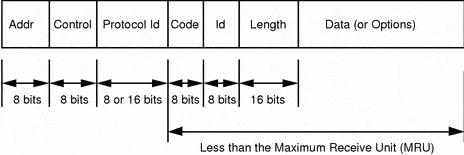
Link Control Protocol (LCP): Mastering PPP Link Management
Uncover the essentials of Link Control Protocol (LCP), a crucial subprotocol of PPP for effective network link management.
-
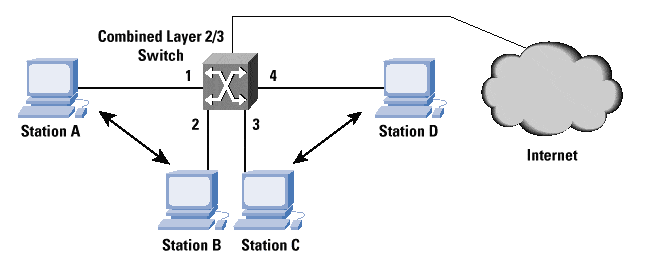
Layer 3 Switch
Layer 3 switch is an Ethernet switch that switches packets by looking at both their network address (for example, their IP or IPX address) and their physical address (for example, their MAC address).
-

Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F)
L2F stands for Layer 2 Forwarding, is a media-independent tunneling protocol developed by Cisco Systems.
-
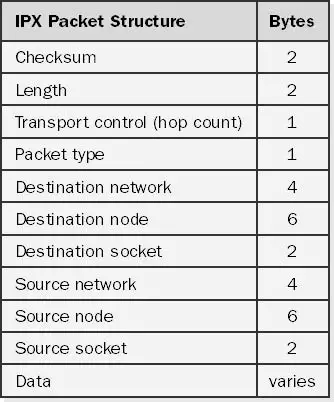
Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX)
IPX is a Novell NetWare protocol used for routing packets from one network node to another throughout an internetwork.
-
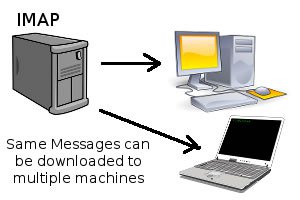
Internet Mail Access Protocol version 4 (IMAP4)
IMAP4 stands for Internet Mail Access Protocol version 4, is an Internet standard protocol for storing and retrieving messages from Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) hosts.
-
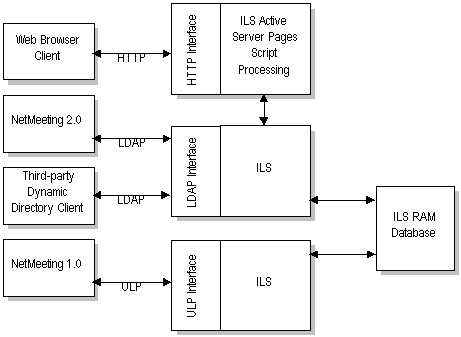
Internet Locator Service (ILS)
Explore the origins and functions of Internet Locator Service (ILS), the LDAP-based directory service once pivotal in Microsoft NetMeeting.
