Our Latest Articles
-
Category 5 cabling
Category 5 cabling is a level 5 grade of unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling.
-
Twisted Pair Cable: Unraveling the Essentials of Network Wiring
Explore the world of twisted pair cable, a cornerstone of network wiring, from its history to types and industry standards. Essential reading for network professionals.
-

Unshielded Twisted-pair (UTP) Cabling
Unshielded Twisted-pair Cabling, or UTP cabling, is Twisted-pair cabling with no internal shielding.
-
STP Cable: Your Shield Against Network Disturbances
Discover the intricacies of STP Cable – from its design to performance in securing network communications. Dive deep into the world of shielded cabling.
-
Server Service
Server Service, also known as LanmanServer, a component of the Microsoft Windows Server operating systems that allows a server to share file and print resources with clients over the network.
-

Server-Based Network: Everything You Need To Know
This article dives deep into the nuances of server-based networks, unraveling their importance in enhancing both security and efficiency. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced benefits, we cover it all. Are you ready to transform your network management strategy?
-

Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (S-HTTP)
Unveil the essentials of S-HTTP, the protocol for encrypting HTTP traffic. Explore its creation, functionality, current usage, and comparison with HTTPS.
-
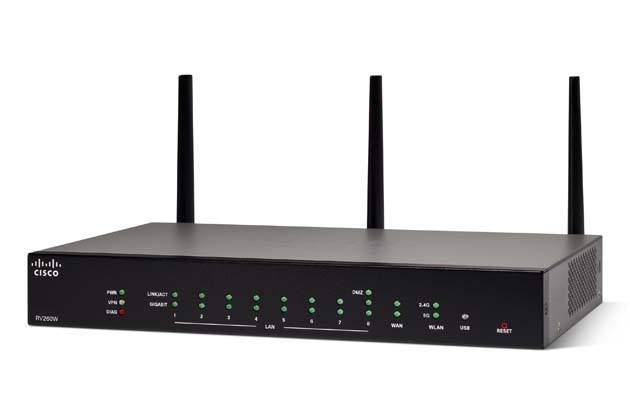

Router
ROUTER is a networking device that is used to extend or segment networks by forwarding packets from one logical network to another.
-
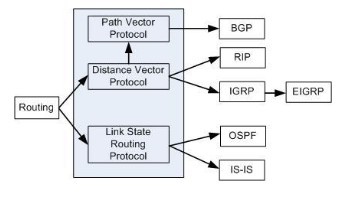
Routing Protocol
Routing Protocol is a protocol that enables the exchange of routing tables between routers in an internetwork.
-
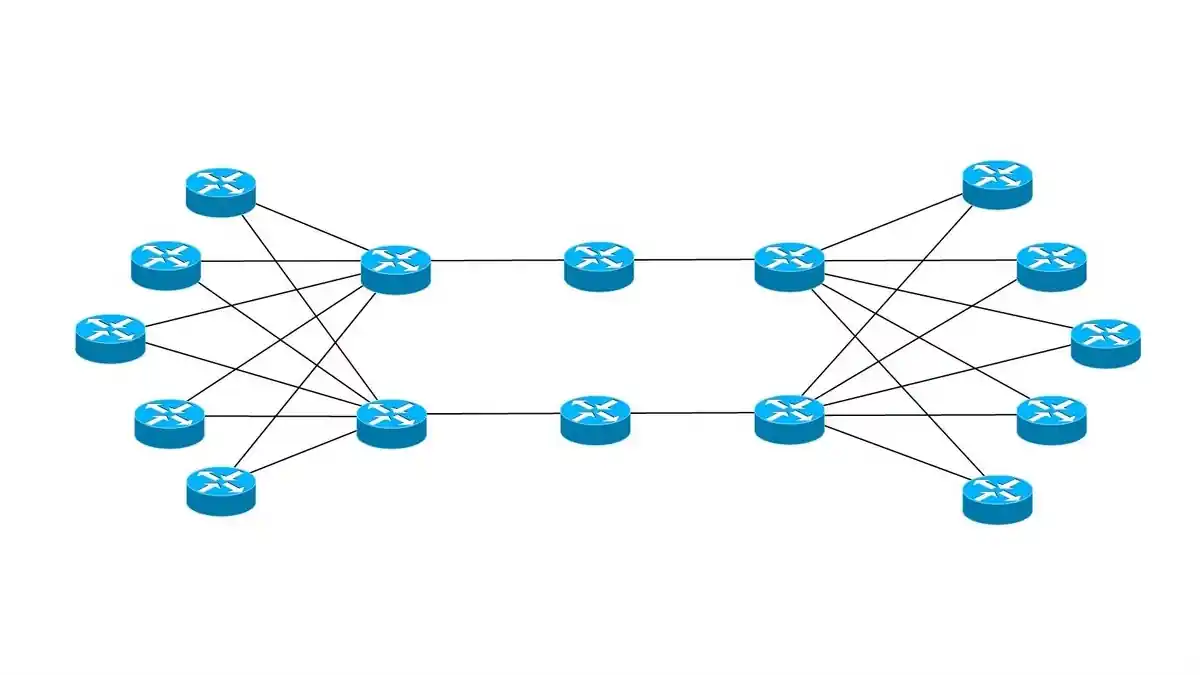
Routing Algorithm
Dive deep into the fascinating world of the routing algorithm! Uncover its secrets, classifications, and why it’s the linchpin of modern networks.
-

Routing (in TCP/IP Networks)
ROUTING is the process of selecting a path through an internetwork over which to transmit packets to a destination host or hosts and then having devices called routers forward the packets to those hosts.