Understanding network topologies is a cornerstone for anyone delving into the realms of computer science and network administration. Star Bus topology, a hybrid networking configuration, combines the strengths of both star and bus topologies to offer unique advantages. In this updated and comprehensive guide, we’ll cover what a Star Bus topology is, the types of cables you can use, and how to optimize its performance for today’s networking environments. Ideal for computer science and network administration students, this article aims to be your go-to resource on the subject.
In this article:
What is Star Bus Topology?
Star Bus topology is a sophisticated networking architecture that fuses the star and bus topologies to form a robust, single network.
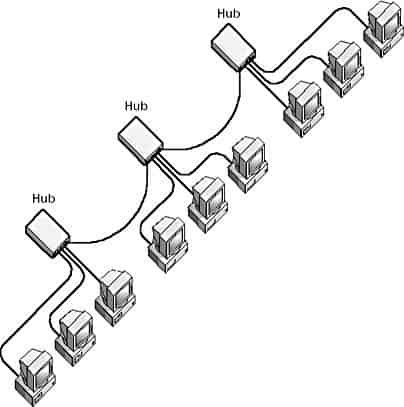
At its core, multiple hubs or switches (often representing departmental or workgroup local area networks) are interconnected using a central bus-like backbone. This layered approach offers the centralized management features of a star topology along with the simplified cable layout and fault tolerance of a bus topology.
Cable Options
When constructing a Star Bus topology network, cable choice is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Various factors, such as the type of hubs or switches you’re using and the desired performance, come into play. Here’s a more detailed look at the types of cables you can use for connecting hubs or switches in a Star Bus network:
Regular 10Base2 or 10BaseT Cables with Uplink Ports
- What They Are: These are Ethernet cables conforming to the 10Base2 or 10BaseT standards. 10Base2 cables are coaxial cables, while 10BaseT cables are twisted-pair cables.
- When to Use: Opt for these if your hub or switch comes equipped with uplink ports. Uplink ports allow for an easier and more straightforward connection to other hubs or switches, facilitating the expansion of your network.
- Advantages: These standard cables are widely available and relatively inexpensive. They also benefit from a well-established ecosystem, which makes compatibility less of an issue.
Crossover Cables
- What They Are: Crossover cables are a type of Ethernet cable where the sending and receiving wires are crossed, effectively enabling two devices to communicate without a hub or switch in between.
- When to Use: These cables are most suitable when you’re connecting regular host ports on two different hubs or switches, and neither of them has an uplink port.
- Advantages: Crossover cables allow for a direct, peer-to-peer connection between hubs or switches, eliminating the need for an extra networking device. This can simplify network setup in certain scenarios.
Special Stackable Cables
- What They Are: These are unique, proprietary cables designed for stackable hubs or switches.
- When to Use: These cables are essential if you’re using stackable hubs or switches that are designed to work in tandem, effectively operating as a single unit.
- Advantages: Using stackable cables allows you to manage multiple hubs or switches as if they were one, streamlining administration tasks. This cable type also paves the way for seamless scalability, as you can easily add more hubs or switches to the stack as your network grows.
By taking the time to choose the appropriate cable type for your Star Bus topology, you ensure not only the functionality but also the efficiency and scalability of your network. Keep in mind that the best choice may vary depending on your specific needs and existing network infrastructure.
Performance Optimization Tips
Optimizing the performance of a Star Bus topology is crucial to ensure a seamless, efficient network experience. Here are some detailed tips for elevating the performance of your network:
Avoid Large Collision Domains
- What it Means: A collision domain is a network segment where data packets can collide with one another when being sent simultaneously.
- Action: If you’re using Ethernet hubs, keep the number of stations to a minimum to reduce the risk of collisions.
Use Bridges or Routers
- What They Do: Bridges and routers can segment the network, thereby breaking up collision domains.
- Advantages: These devices isolate traffic, improve bandwidth utilization, and can even filter data to improve security and performance.
Network Monitoring
- Importance: Constantly monitoring your network can help you detect bottlenecks and potential points of failure early on.
- Tools: Utilize network monitoring software that can provide real-time analytics and suggest optimizations.
Prioritize Traffic
- Why: Not all data packets are equal. Some are more urgent than others, like VoIP traffic or video conferencing data.
- How: Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings in your routers or switches to prioritize essential traffic and ensure it doesn’t get delayed or dropped.
Modern Relevance
The Star Bus topology has evolved over the years, partly owing to technological advancements and partly due to the changing needs of modern networks.
Adaptability
- Why it Matters: Modern networks need to be flexible and scalable, features intrinsic to the Star Bus topology.
IoT Integration
- Current Trend: With the advent of IoT devices, network topologies have had to adapt to an influx of a variety of devices. Star Bus topology can handle this variety better than older, more rigid topologies.
Hybrid Models
- Evolution: The concept of the Star Bus topology is often merged with other topological designs to create hybrid models that serve very specific needs in modern business environments.
Legacy Systems
- Still Relevant: While not as commonly used as before, the Star Bus topology remains relevant, especially in settings where legacy systems are operational and migrating to a newer topology is cost-prohibitive.
References
Books:
- “Computer Networks” by Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall
- “Network Warrior” by Gary A. Donahue
Websites:
- Cisco Networking Academy – Star, Bus, Ring and Hybrid topologies
- Network Computing – Network Topology Guide
Network Encyclopedia Articles: