A Channel Service Unit (CSU) is a critical device in digital communication, connecting digital lines to network equipment. It plays a key role in integrating local networks with broader telecommunication services, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission.
Table of Contents
- What is a Channel Service Unit (CSU)?
- How it works
- CSUs and DSUs Combined
- The Legacy of CSU Devices
- References

1. What is a Channel Service Unit
Definition and Purpose
A Channel Service Unit, or CSU, is a digital communication device designed to connect a digital line, such as Digital Data Service (DDS), T-carrier services like a T1 line, or Frame Relay links, to a digital device. Its primary purpose is to facilitate the connection between local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs) through telecommunication carrier services. The CSU acts as an intermediary that not only ensures the proper transmission of data across different networks but also safeguards the integrity and security of the data being transferred.
Role in Telecommunications
In the telecommunications landscape, the CSU serves several crucial functions:
- Loopback Testing: The CSU is capable of performing loopback testing, a diagnostic technique used to test the transmission and reception of signals. This testing helps in identifying and troubleshooting faults in the communication line, ensuring the network’s reliability and performance.
- Bit Stuffing: Some CSUs may perform bit stuffing, which involves adding non-informational bits into the data stream to ensure synchronization between transmitting and receiving ends. This process helps in maintaining the integrity of the transmitted data over digital networks.
- Framing and Formatting: CSUs can provide framing and formatting patterns compatible with the network. This ensures that the data conforms to specific standards required for transmission over T-carrier systems, facilitating seamless integration with telecommunication networks.
- Electrical Interference Barrier: The device acts as a barrier for electrical interference, protecting the network from potential disruptions that could affect data transmission. This feature is essential for maintaining high-quality communication channels.
- Signal Regeneration: Positioned as the last signal regeneration point before the signal reaches a multiplexer or data terminal equipment (DTE), the CSU plays a vital role in enhancing signal strength. It regenerates the signal coming from the central office, ensuring that it remains strong and clear up to its final destination.
The Channel Service Unit’s role in telecommunications is indispensable, providing the necessary interface, protection, and signal management to maintain robust and secure digital communication networks. Through its various functionalities, the CSU ensures that LANs can effectively integrate into WANs, leveraging telecommunications carrier services to extend network reach and capabilities.
2. How it Works
Technical Overview
The Channel Service Unit (CSU) is a pivotal device in terminating the end of a digital telecommunications line at the customer premises. It directly interfaces with Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) devices, such as routers, switches, multiplexers (MUX), or dedicated servers, establishing a critical connection point for digital data transmission. The primary function of the CSU is to ensure that the digital signal transmitted across the telecommunications line is properly terminated and ready for use by the DTE devices.
Connection to a DTE typically utilizes RS-232 or V.35 serial transmission interfaces, which are standard protocols for serial data communication. This setup allows for the seamless transmission of data between the CSU and the DTE, facilitating reliable and efficient communication.
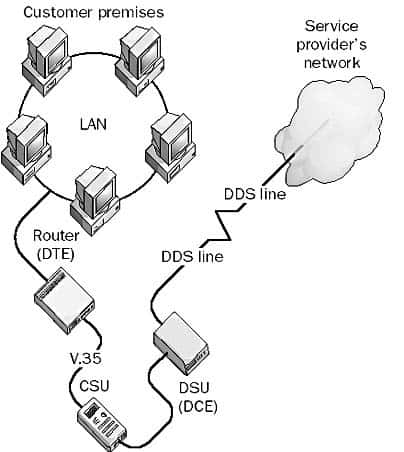
On the service provider side, the CSU must connect to a Data Service Unit (DSU), another essential piece of data communications equipment (DCE). The DSU is responsible for converting the digital signals into a format that is suitable for transmission over the telecommunications line. It also plays a vital role in creating and maintaining the connection, ensuring continuous and stable communication.
Telecommunications service providers often lease CSUs to customers, preconfigured for the specific type of communications support required. This arrangement simplifies the setup process for customers and ensures compatibility with the service provider’s network.
Functions and Features
CSUs come equipped with a range of functions and features designed to enhance the reliability and manageability of digital telecommunications:
- Remote Diagnostic Capabilities: Many CSUs include features for remote diagnostics, such as remote loop testing. This allows for the identification and troubleshooting of issues from a distance, minimizing downtime and the need for onsite technical support.
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Features: Some CSUs support SNMP, a protocol used for network management. This feature enables the service provider to monitor the status and performance of the CSU remotely, ensuring optimal operation and quickly addressing any potential issues.
These features not only streamline the management of digital telecommunications but also enhance the overall reliability and quality of the connection.
3. CSUs and DSUs Combined
The Synergy between CSU and DSU
In modern telecommunications setups, CSUs are often combined with DSUs to form a single unit known as a CSU/DSU. This integration streamlines the connection process by consolidating the functions of both devices into one, simplifying the network architecture and reducing the complexity of managing separate devices.
Benefits of Integration
The combination of CSU and DSU devices into a single unit offers several significant benefits:
- Simplified Setup and Configuration: By integrating the CSU and DSU, the setup process becomes more straightforward, requiring less time and technical expertise to establish a functional telecommunications link.
- Reduced Equipment Needs: A combined CSU/DSU device reduces the physical space and power requirements compared to using separate units, making it an efficient choice for many organizations.
- Enhanced Compatibility: Integrated CSU/DSU devices are designed to work seamlessly with a wide range of telecommunications services and DTE devices, ensuring broad compatibility and flexibility in various network environments.
- Cost Efficiency: The consolidation into a single device can be more cost-effective, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance and support.
Dedicated stand-alone CSUs are now typically reserved for specific scenarios where customer premises telecommunications equipment already contains integrated DSUs, such as channel banks, Private Branch Exchanges (PBX), T1 multiplexers, or other specialized devices. This setup ensures that organizations can leverage existing infrastructure while benefiting from the advanced features and capabilities of modern CSU/DSU devices.
4. The Legacy of CSU Devices
Historical Context
The inception of Channel Service Unit (CSU) devices traces back to the early days of digital telecommunications, a time when the transition from analog to digital communications required new infrastructure and equipment. Initially developed to facilitate reliable digital connections over telephone lines, CSUs became a cornerstone in the burgeoning field of digital networking. Their role was to ensure that digital signals could be accurately transmitted and received over the existing telecommunications infrastructure, which was predominantly designed for analog voice communication.
Evolution and Impact on Modern Networking
Over the years, CSUs have undergone significant evolution, adapting to the changing landscapes of technology and telecommunications. From bulky, standalone units to integrated CSU/DSU devices, their design and functionality have evolved to meet the demands of increasing data rates and the need for more sophisticated network management and diagnostics.
The impact of CSU devices on modern networking cannot be overstated. They laid the groundwork for the widespread adoption of digital communications, enabling businesses and consumers to leverage the speed and efficiency of digital data transmission. Today, while the technology has continued to advance and the specific role of traditional CSUs has diminished in favor of more integrated networking solutions, the principles of reliable, secure, and manageable digital communication that they introduced remain at the heart of contemporary networking technologies.
5. References
Books
- “Data Communications and Networking” by Behrouz A. Forouzan. This book provides a comprehensive overview of the principles of data communication, including the role and functioning of CSUs in digital networks.
- “Telecommunications Essentials, Second Edition: The Complete Global Source” by Lillian Goleniewski. This resource offers insights into the evolution of telecommunications equipment, including CSUs, and their impact on the development of networking.
Technical Documents
- RFC 1332 – The PPP Internet Protocol Control Protocol (IPCP). This document, while focused on PPP, provides context for the environment in which CSUs operate and the technical requirements for data transmission over digital lines.
- Federal Standard 1037C