Home Folder, also called home directory, is a user’s private folder for storing personal files.
What is Home Folder?
Also called home directory, a user’s private folder for storing personal files. Home folders for users are usually centrally located on a network server for the following reasons:
- To ensure that their contents are backed up regularly
- To make home folders available from any computer on the network
- To make home folders available from any client operating system
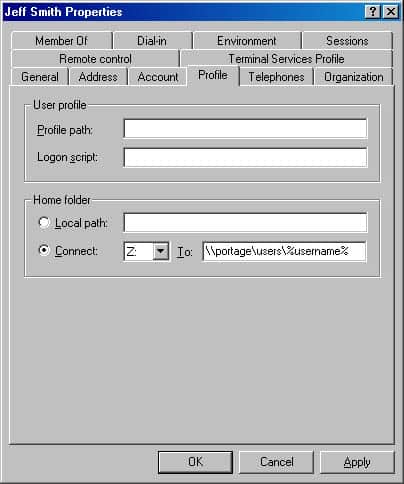
Assign a home folder to a local user
To assign a home folder to a local user:
- Click Start, click Control Panel, double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Computer Management.
- In the console tree, click Users in Local Users and Groups.
- Click the user account.
- Click the Action menu, and then click Properties.
- Click the Profile tab, click Connect, and then specify a drive letter.
- In the To box, type a path. This path can be any of the following types:
- Network path, for example:\\server\users\tester
- You can substitute username for the last subfolder in the path, for example:\\server\users\username
Where server is the name of the file server housing the home folders, and where users is the shared folder.
- Click OK.
Assign a home folder to a domain user
Note: To specify a network path for the home folder, you must first create the network share and set permissions that permit the user access. You can do this with Shared Folders in Computer Management on the server computer.
To assign a home folder to a domain user:
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Active Directory Users and Computers.
- In the console tree, click Users.
- In the Details pane, right-click the user account, and then click Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box, click Profile.
- Under the Home folder, type the folder information. To do this, follow these steps:
- To assign a home folder on a network server, click Connect, and then specify a drive letter.
- In the To box, type a path. This path can be any one of the following types:
- Network path, for example:\\server\users\tester
- You can substitute username for the last subfolder in the path, for example:\\server\users\usernameNote In these examples, server is the name of the file server housing the home folders, and users is the shared folder.
- Click OK.
Home Folder in Windows NT
Microsoft Windows NT Server does not have a default location for home folders. To create a network share for users’ home folders on a Windows NT-based network, follow these steps:
- Use Windows Explorer on a server to create and share a folder called Users on a volume formatted using the NTFS file system of the server on which users’ home folders will be stored. The home folders will all be located in the Users share.
- Remove the default Full Control access for Everyone and assign Full Control to Users. This restricts access to the shared folder to domain users.
- Use the Profiles button on the User Properties dialog box in User Manager for Domains, and specify the location of each user’s home directory using the format \\SERVER_NAME\users\%username%. The expression %username% is an environment variable that will be replaced with the account name for each user. A subfolder within the Users share will be created for each user; this subfolder will be the user’s home folder, and its name will be the same as the user’s account name. Each user will have Full Control access on his or her home folder; no other user, including Administrator, will have permissions on the folder.
NOTE
Home folders are not part of the user profile of roaming users, so they must be specified as described in this entry. In Windows 2000, use Computer Management to assign home folder locations. Open the property sheet for the user and specify the location of the user’s home folder on the Profile tab (see the screen capture on the previous page).