Intermediary devices play a crucial role in the realm of computer networking. These devices, often unnoticed, are instrumental in managing and directing data as it flows across a network. From routers and switches to modems and firewalls, intermediary devices ensure that data packets travel from their source to their destination efficiently and securely.
This article aims to demystify the concept of intermediary devices, exploring their various types, functionalities, and importance in modern network infrastructures.
In this article:
- What is an Intermediary Device?
- Intermediary Device Examples
- How Intermediary Devices Enhance Network Performance
- Configuring and Managing Intermediary Devices
- Trends and Future of Intermediary Devices
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- References and Further Reading

1. What is an Intermediary Device?
Definition and Role in Networking
In the context of computer networking, an intermediary device refers to any hardware used to connect multiple network segments or devices, facilitating the flow of data. These devices are essential components of a network, acting as mediators or ‘middlemen’ in the process of data transmission.
Their primary role is to ensure that data packets are appropriately routed and delivered from the source to the destination. Intermediary devices analyze, process, and forward data, playing a critical role in maintaining the overall health and efficiency of the network.
Key Functions and Operations
- Data Routing and Switching: Intermediary devices determine the best path for data packets to travel across a network, efficiently managing the data traffic to avoid congestion and delays.
- Data Processing: They process network protocols, encapsulate data for transmission, and convert signals as necessary for different network environments.
- Network Management: These devices monitor network traffic, diagnose problems, and dynamically adjust to network changes to optimize performance.
- Security Implementation: Many intermediary devices have built-in features to enforce security policies, filter traffic, and protect the network from external threats.
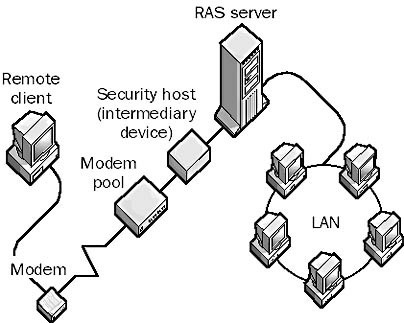
See also: Security Devices in Networking.
2. Intermediary Device Examples
Routers: Directing Traffic Across Networks
Routers connect different network segments, directing data packets based on their destination IP addresses. They are crucial in determining the most efficient route for data to travel between networks, including the Internet.
Switches: Managing Data Flows within Networks
Switches operate within a single network segment, directing data packets specifically to the devices within the network, rather than broadcasting to all connected devices. They enhance network efficiency and reduce unnecessary traffic.
Modems: Facilitating Internet Connectivity
Modems (modulator-demodulator) convert digital data from a computer into analog signals suitable for transmission over telephone lines, and vice versa, enabling internet connectivity.
Firewalls: Securing Network Boundaries
Firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. They act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks.
Network Bridges and Repeaters
Bridges connect multiple network segments, operating at the data link layer, while repeaters regenerate or amplify signals to extend the transmission distance over a network.
3. How Intermediary Devices Enhance Network Performance
Improving Data Transmission Efficiency
Intermediary devices optimize the data flow, reducing transmission times and increasing the overall speed of the network. They efficiently manage bandwidth and prevent data collisions.
Ensuring Network Security and Integrity
Through features like firewalls and encryption, these devices play a vital role in securing the network, preventing unauthorized access, and maintaining data integrity.
Balancing Network Load
Intermediary devices distribute network traffic evenly, preventing overloading of any single resource. This load balancing is crucial in large networks to maintain consistent performance and availability.
In summary, intermediary devices form the backbone of modern networking, ensuring efficient, secure, and reliable data transmission across various network segments. Understanding their functions, operations, and examples helps in appreciating their indispensable role in today’s interconnected world.
4. Configuring and Managing Intermediary Devices
Basic Setup and Configuration Tips
- Understanding Device Specifications: Before setting up, understand the capabilities and limitations of your intermediary device. Ensure it meets the network’s bandwidth, security, and protocol requirements.
- Default Settings: Start with factory settings. Many devices come with a default configuration that can be used as a starting point.
- Firmware Updates: Always update the device’s firmware to the latest version. This ensures you have the latest features and security updates.
- Configuring Network Parameters: Set up network parameters like IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateways according to your network design.
- Security Settings: Configure necessary security settings, including firewalls, access control lists (ACLs), and encryption standards to protect the network.
Monitoring and Maintenance Best Practices
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor network performance and traffic. Tools like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) can be used for real-time monitoring.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance checks to ensure devices are functioning optimally. This includes checking for firmware updates, reviewing security settings, and verifying network configurations.
- Performance Benchmarks: Establish performance benchmarks and regularly compare actual performance to ensure the network is operating efficiently.
- Backup Configurations: Regularly back up current configurations. In the event of a device failure, this will allow for quick restoration.
5. Trends and Future of Intermediary Devices
Evolving Technologies in Networking
- Advanced Data Processing: With increasing data volumes, intermediary devices are evolving to offer more advanced data processing capabilities, including deep packet inspection and real-time analytics.
- Automation and AI: The integration of AI and machine learning for automated network management is becoming more prevalent, enabling smarter, self-optimizing networks.
The Impact of IoT and Cloud Computing
- IoT Device Management: As the number of IoT devices grows, intermediary devices are adapting to manage and secure these new endpoints.
- Cloud Integration: The rise of cloud computing is driving the need for intermediary devices that can efficiently connect and manage cloud-based resources and services.
6. Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Illustrative Examples of Intermediary Devices in Action
- Healthcare: Hospitals use routers and switches to manage patient data flow, ensuring reliable and secure communication between various departments and devices.
- Retail: In retail, intermediary devices like wireless access points and firewalls are used to manage online transactions, ensuring customer data security and seamless online shopping experiences.
How Different Industries Leverage These Devices for Network Optimization
- Manufacturing: Advanced routers and switches are used in manufacturing for real-time monitoring and control of production processes.
- Education: Educational institutions utilize intermediary devices to manage and secure their campus networks, supporting e-learning and online resources.
7. References and Further Reading
- Books:
- “Computer Networks” by Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall.
- “Network Warrior” by Gary A. Donahue.
- Online Resources:
- Cisco’s official networking blogs and documentation.
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library for technical papers on networking technologies.
- Industry Publications:
- “Network World” and “PCMag” for the latest trends and reviews in network technologies.
- Case studies published by major network equipment manufacturers like Cisco and Juniper Networks.