The World Wide Web Publishing Service (WWWPS) is a critical component in the architecture of web hosting and management on Windows servers. It plays a pivotal role in facilitating the hosting and delivery of web content. This article delves into what WWWPS is, its functionalities, historical context, and its significance in the broader landscape of web technologies. By understanding WWWPS, readers will gain insights into the foundational services that support web applications and sites, illustrating its importance in the digital age.
Table of Contents:
- What is the World Wide Web Publishing Service?
- Historical Overview and Evolution
- Core Functionalities and Features
- World Wide Web Publishing Services Properties
- The Role of WWWPS in Web Hosting and Management
- Comparing WWWPS with Other Web Services
- References

1. What is the World Wide Web Publishing Service?
The World Wide Web Publishing Service (WWWPS) is a feature of the Internet Information Services (IIS), which is included with Windows Server operating systems. It is responsible for managing the delivery of web content on the internet. WWWPS enables web servers to host websites, providing the necessary infrastructure for web applications and services to run efficiently. It handles HTTP requests from clients, serving web pages and applications to users across the globe.
2. Historical Overview and Evolution
Introduced with early versions of IIS, WWWPS has evolved significantly over the years. Its inception was aimed at providing a scalable, reliable platform for web publishing, a necessity with the burgeoning growth of the internet in the 1990s. Over time, Microsoft has updated WWWPS to include support for newer protocols, enhance security features, and improve performance and scalability. This evolution reflects the changing landscape of web technology and the increasing demands for more sophisticated web hosting solutions.
3. Core Functionalities and Features
The World Wide Web Publishing Service (WWWPS) is a fundamental component of Internet Information Services (IIS) on Windows Server, providing a robust framework for web hosting and management. This service underpins the operation of websites and web applications by handling HTTP requests, managing domains, and ensuring secure and efficient content delivery. Here, we delve into the core functionalities and features that define WWWPS, illustrating how it operates within the IIS ecosystem to facilitate web publishing and hosting.
HTTP Request Processing
- Connection Management: WWWPS manages the connections between web clients and the server, handling the complexities of connection pooling, keep-alive connections, and HTTP/2 multiplexing. This ensures efficient use of server resources and faster response times for clients.
- Request Handling: It interprets HTTP requests, routes them to the appropriate website or application, and manages the execution of request handlers. This includes serving static content, executing server-side scripts, and invoking web applications.
Security and Authentication
- SSL/TLS Support: WWWPS integrates with IIS to provide secure connections through SSL/TLS, encrypting data transmitted between the web server and clients. This is crucial for protecting sensitive information and ensuring data integrity.
- Authentication Mechanisms: It supports a variety of authentication methods, including Anonymous, Basic, Windows (NTLM), and Kerberos authentication, allowing web administrators to control access based on user identity.
- Authorization and Access Control: WWWPS enables fine-grained access control to resources, allowing administrators to specify permissions at the site, folder, or file level. It works in tandem with IIS to enforce these permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access or modify web content.
Site and Application Management
- Application Pools: A key feature of WWWPS is its use of application pools, which isolate web applications into separate processes. This isolation improves application security, stability, and performance by preventing applications from affecting each other.
- Site Bindings: WWWPS allows administrators to configure site bindings, specifying the IP addresses, ports, and hostnames that a site responds to. This facilitates hosting multiple websites on a single server and managing SSL certificates for secure sites.
Performance Optimization
- Output Caching: To enhance performance, WWWPS can cache dynamic and static content, reducing server load and improving response times for subsequent requests. Cached content is served directly from memory, bypassing the need for processing.
- Compression: It supports dynamic and static compression of HTTP responses, reducing bandwidth usage and speeding up content delivery to clients. Compression settings can be fine-tuned to balance performance and resource usage.
Scalability and Reliability
- Load Balancing: While WWWPS itself does not provide load balancing, it is designed to work seamlessly with load balancers and web farms, distributing requests across multiple servers to enhance scalability and reliability.
- Health Monitoring and Recovery: WWWPS integrates with IIS’s health monitoring features, automatically restarting failed worker processes and application pools to maintain service availability.
The World Wide Web Publishing Service encapsulates these core functionalities, offering a comprehensive platform for web hosting and management. By leveraging these features, administrators can deploy and manage web applications and sites efficiently, ensuring they are secure, performant, and highly available. This deep dive into the workings of WWWPS reveals the sophisticated mechanisms at play, facilitating a smooth and reliable web experience for users and administrators alike.
4. World Wide Web Publishing Services Properties
To verify that the World Wide Web Publishing Service is installed and not disabled:
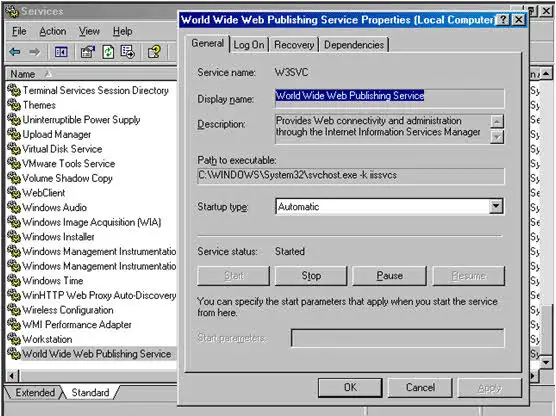
- Right-click My Computer on the desktop, and then click Manage.
- Expand the Services and Applications node, and then click the Services node.
- In the right pane, locate the World Wide Web Publishing Service.
- If the World Wide Web Publishing Service is not displayed in the list of services installed, follow the steps in the procedure below to install it.
- If the World Wide Web Publishing Service is displayed but has a status other than Started, continue with the steps below to start it.
- Right-click World Wide Web Publishing Service, and then click Properties.
- Verify the Startup Type is Automatic and the Service status is set to Started.
- Click Apply, and then click OK.
5. The Role of WWWPS in Web Hosting and Management
The World Wide Web Publishing Service (WWWPS) plays a pivotal role in the ecosystem of web hosting and management, especially within the Windows Server environment. Its integration with Internet Information Services (IIS) enables administrators and developers to deploy, host, and manage web applications and sites with efficiency and precision. Below are key aspects highlighting the importance of WWWPS in web hosting and management:
Centralized Web Server Management
- Unified Interface: WWWPS, through IIS Manager, provides a unified interface for configuring web servers, websites, and applications. This centralization simplifies the management tasks, allowing for the easy setup of new sites, application pools, and security settings.
Enhanced Security
- Comprehensive Security Features: WWWPS offers a suite of security features, including encryption with SSL/TLS, authentication mechanisms, and authorization controls. These features ensure that web applications and sites are secure against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Scalability and Performance
- Resource Optimization: By managing application pools and utilizing caching and compression techniques, WWWPS optimizes resource usage, enhancing the scalability and performance of web applications. This is crucial for handling varying traffic loads and ensuring a smooth user experience.
Reliability and Availability
- Health Monitoring and Automatic Recovery: The service monitors the health of web applications and automatically recovers from service disruptions. This ensures high availability and reliability of hosted applications, minimizing downtime.
6. Comparing WWWPS with Other Web Services
WWWPS, as part of IIS, offers a comprehensive set of features for web hosting and management. However, it’s important to compare it with other web services to understand its place in the broader web hosting landscape:
Apache HTTP Server
- Cross-Platform Support: Unlike WWWPS, which is tailored for Windows environments, Apache HTTP Server offers broad cross-platform support, running on various Unix/Linux, macOS, and Windows systems.
- Flexibility and Modularity: Apache is known for its modularity, allowing users to extend its functionality with a wide range of modules for security, caching, URL rewriting, and more.
Nginx
- Performance and Efficiency: Nginx is renowned for its high performance, especially in handling static content and reverse proxy configurations, with a strong focus on low memory usage.
- Asynchronous Architecture: Its event-driven architecture allows handling thousands of concurrent connections in a single process, making it particularly effective for high-traffic websites.
Comparison Summary
While Apache and Nginx offer flexibility and performance, especially in Unix/Linux environments, WWWPS integrates deeply with Windows Server features, providing a seamless web hosting solution for Windows-based applications. Its tight integration with Windows security, management tools, and Active Directory makes it a preferred choice for Windows-centric environments.
7. References
- Microsoft Documentation on IIS: Offers comprehensive guides, tutorials, and reference materials for Internet Information Services (IIS) and the World Wide Web Publishing Service.
- RFC 2616 – Hypertext Transfer Protocol — HTTP/1.1: Provides the foundational standards for web communications and services.