Category: Letter A
-

Understanding Authentication in Networking
Delve into the essentials of authentication in networking, ensuring secure access and protecting digital identities in the connected world.
-
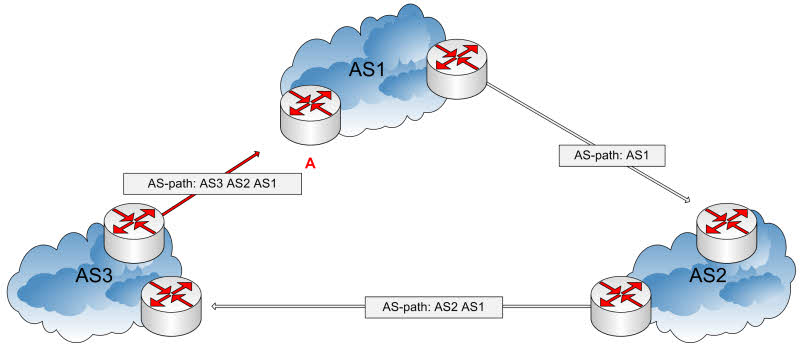
Autonomous System (AS)
The internet is not just one big network. There are millions of autonomous systems that cooperate to route IP packets. Read this article to fully understand this concept.
-
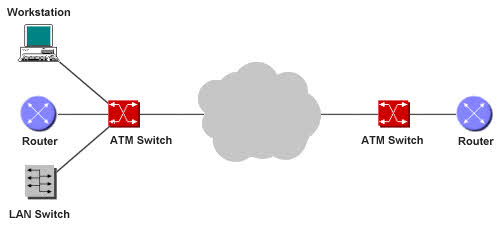
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, is a high-speed, broadband transmission data communication technology based on packet switching, which is used by telcos, long distance carriers, and campus-wide backbone networks to carry integrated data, voice, and video information.
-
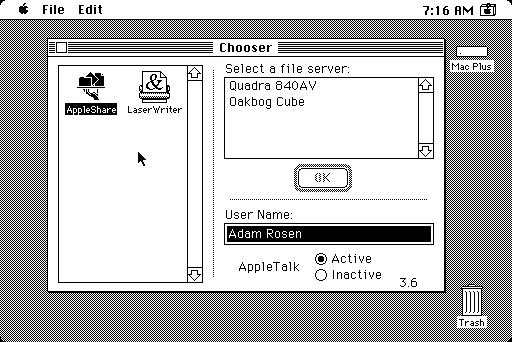
AppleTalk: Understanding the Legacy Networking Protocol for Apple Devices
Explore the history and architecture of AppleTalk, the foundational networking protocol for early Apple devices, and its evolution into modern technologies.
-
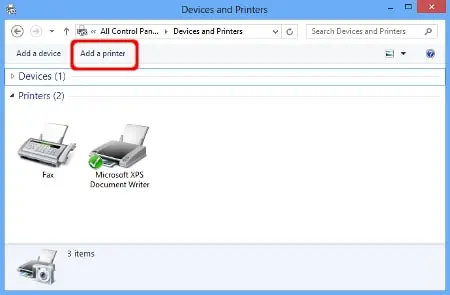
Add Printer
When you connect a printer to your PC or add a new printer to your home network, you can usually start printing right away. Windows supports most printers, and you probably won’t have to go out of your way to install special printer software. If you’re using Windows 8.1 or Windows RT 8.1, additional printer…
-
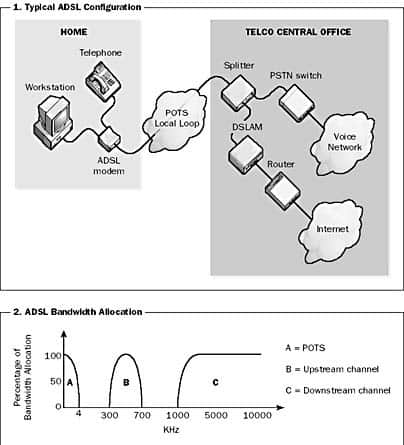
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
ADSL stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line, is a telco service that provides subscribers with high-speed digital telephone services.
-
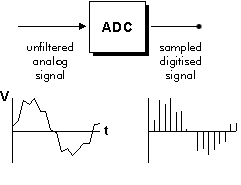
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
ADC stands for Analog-To-Digital Converter, is any device for changing analog signals into digital transmission – for example, recording someone singing onto a CD.
-
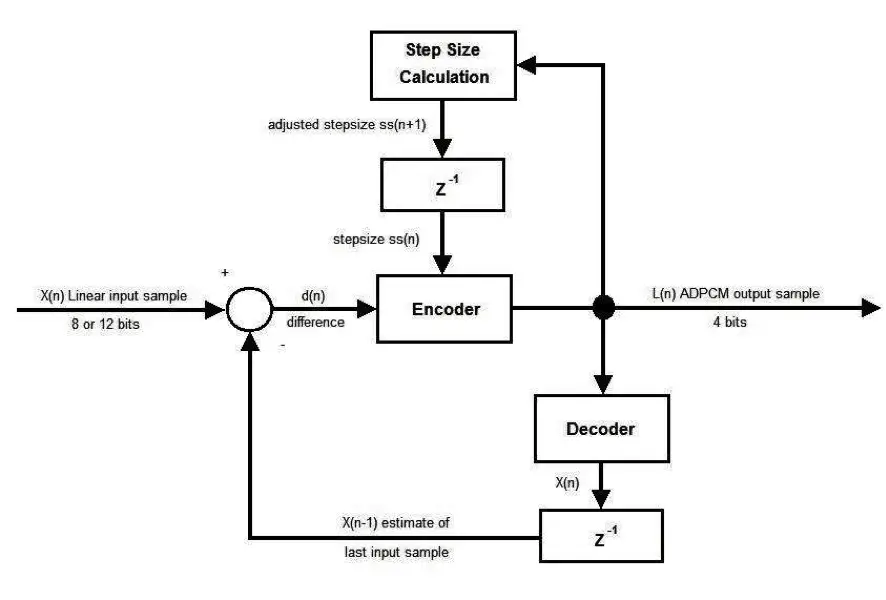
Adaptive Differential Pulse-Code Modulation (ADPCM)
ADPCM stands for Adaptive Differential Pulse-Code Modulation, is a technique for converting analog sound, such as speech, into binary digital information by frequently sampling the sound and expressing its modulation in binary form.
-

Adapter: Bridging the Gap
Dive into the world of network hardware adapters, exploring their vital role in connecting diverse electronic devices for seamless network functionality.
-
ActiveX Data Objects (ADO)
ADO stands for ActiveX Data Objects, is a data access interface used to communicate with OLE DB–compliant data sources.

