Definition of Zone Transfer in Network Encyclopedia.
What is Zone Transfer?
Zone Transfer (in a DNS Server) is the process of transferring information in the zone file on a primary name server to a secondary name server. It is one of several mechanisms available for administrators to replicate DNS databases across a set of DNS servers.
You would do this in the following situations:
- If the primary name server goes down, so that the secondary name server has a complete, up-to-date copy of the zone file and can handle name resolution requests by Domain Name System (DNS) clients on the network.
- If a large number of DNS clients on the local network are making name resolution requests, so that you can load balance these requests between the primary name server and its secondary name servers.
- If the primary name server is located on the other side of a slow wide area network (WAN) link, so that you can reduce network traffic over the link by allowing name resolution requests to be handled locally. The only network traffic created by DNS is occasional zone transfers over the link.
How it works
In Microsoft’s implementation of DNS on Microsoft Windows Server, zone transfers occur in three circumstances:
- When the Microsoft DNS Server Service is started on the secondary name server.
- When the refresh interval for the secondary name server expires – as defined in the start of authority (SOA) record at the beginning of the zone file on the primary name server.
- When changes have been made to the zone file on the primary name server and there is a notify list. The primary name server immediately notifies the secondary name server that the zone file has been modified and instructs it to initiate a zone transfer without waiting for the refresh interval to expire. The notify list is a list of IP addresses that specify which secondary name servers are allowed to access zone information on the primary name server for purposes of zone transfer.
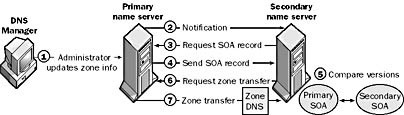
A zone transfer is always initiated by the secondary name server. Typically, the secondary name server periodically contacts the primary name server to determine whether any changes have been made to the primary name server’s zone file. If so, it initiates a request for zone transfer. Specifically, when the refresh interval expires on the secondary name server, the following occurs:
- The secondary name server requests and receives the SOA record from the primary name server.
- The secondary name server compares the version number in the primary name server’s SOA record with its own current version number. If they differ, the secondary name server requests a zone transfer from the primary name server.
- In standard DNS operation, the entire zone file is transferred during this process.
Zone Transfer Limitations
Though it is standardized, full-zone transfer being described as one of the possible database replication mechanisms in RFC 1034 and RFC 5936 (incremental zone transfer described in RFC 1995), zone transfer is the most limited of those database replication mechanisms. Zone transfer operates in terms of “wire format” resource records, i.e. resource records as they are transferred using the DNS protocol. However, the schema of wire format resource records may not be identical to the database schema used by the back ends of the DNS servers themselves.
Zone Transfer Security
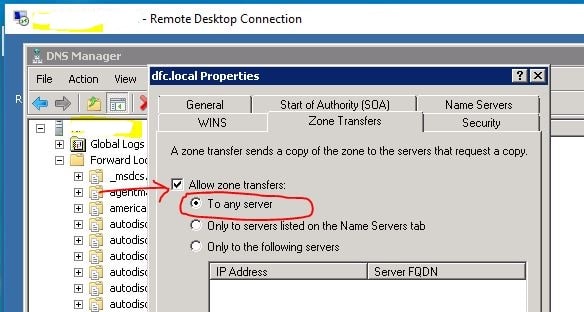
On a Windows Server Operating System, you can specify the servers that are authorized to receive zone transfers for the zone by selecting one of the options on the Zone Transfers tab of the Properties dialog box for the zone.
These options are:
- To any server: enables zone information to replicate to any server.
- Only to servers listed on the Name Servers tab: enables zone information to replicate only to the servers that are listed on the Name Servers tab of the Properties dialog box for the zone. This tab contains a list of servers that are in the same domain as the zone,
- Only to the following servers: specifies whether you want to allow zone transfers only to the servers that you list under IP address on the Zone Transfers tab of the Properties dialog box for the zone.
NOTE
The dynamic update standard supported by Microsoft Windows 2000 allows zone information to be transferred by using updates. The entire contents of the zone file are not sent when a change is made to a resource record in the file. This method is called incremental zone transfer and is defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 1995.
