Category: Network Protocols
-

Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
In this article, we will unravel the layers of Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), exploring its operations, advantages, and its place in the ever-evolving landscape of network security protocols.
-
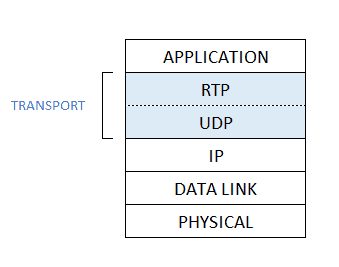
Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP)
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol that provides end-to-end network transport functions suitable for applications transmitting real-time data, such as audio, video, or simulation data, over multicast or unicast network services. In this article: RTP Basics Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) runs on top of UDP. Specifically, audio or video chunks of data,…
-

Computer Networks: A Starter Exploration
Dive into the essentials of computer networks with this authoritative guide, crafted to demystify the complex interactions and technologies that connect computers globally.
-
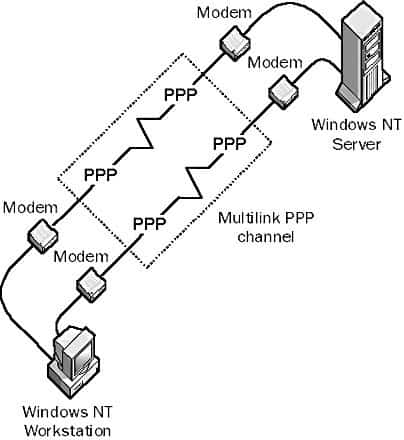
Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol (MPPP)
MPPP which stands for Multilink Point to Point Protocol is a protocol for inverse multiplexing of Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) communication links. Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol (MPPP) is an extension of the industry-standard PPP. MPPP can also be abbreviated as MP or MLP. How it works An ordinary dial-up modem connection to the Internet through an Internet…
-
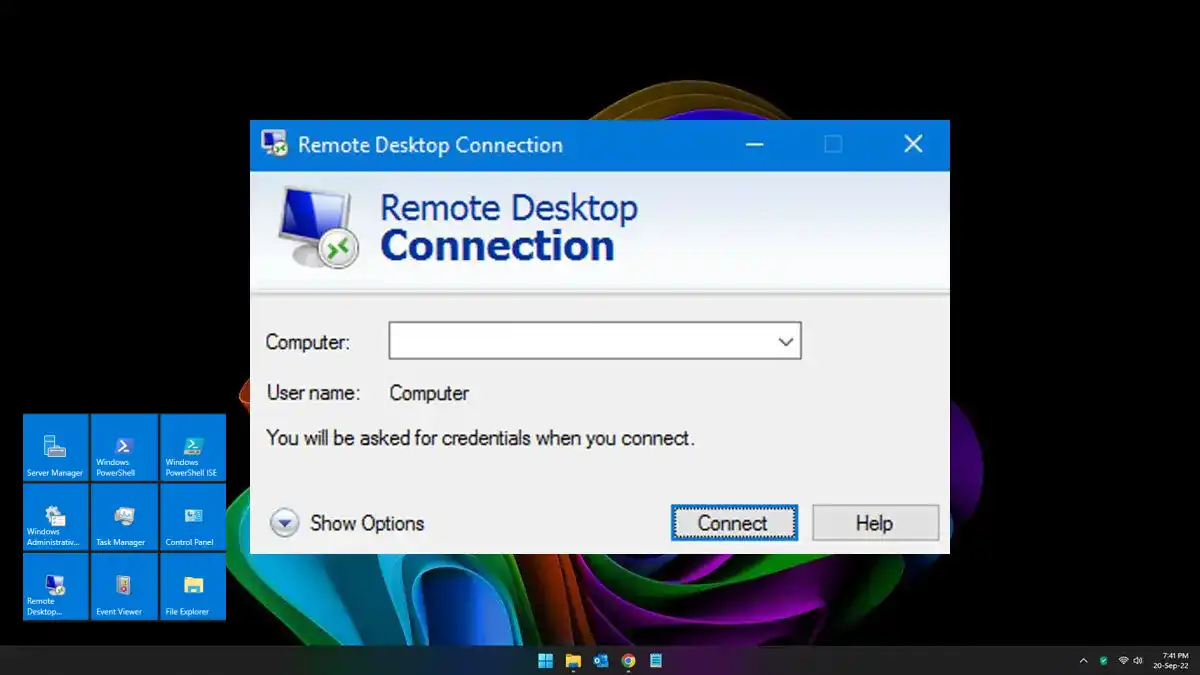
Unpacking Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
Delve into the exciting world of Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), demystifying its functions, applications, and importance in today’s digitally driven era.
-
HTTPS
HTTPS is a protocol developed by Netscape for secure transmission of Web content over the Internet. HTTPS is another name for Netscape’s implementation of the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol that functions as a subprotocol to the application layer (layer 7) protocol, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
-
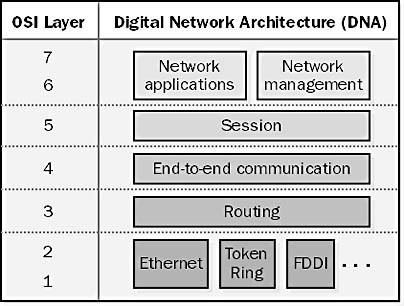
DECnet
Explore DECnet’s role in shaping network architectures, its diverse applications, and enduring influence on modern networking.
-

NWLink IPX/SPX-Compatible Transport
Dive into the world of NWLink IPX/SPX-Compatible Transport, exploring its significance in networking, features, and legacy impact.
-
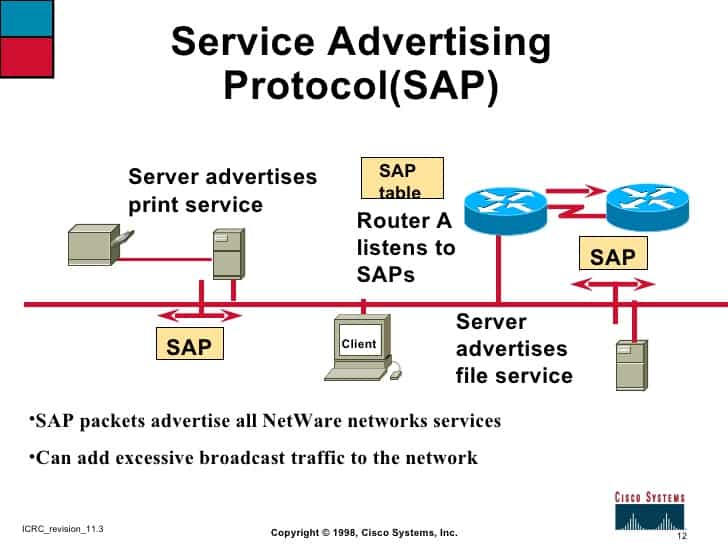
Service Advertising Protocol (SAP)
Service Advertising Protocol, also known as SAP, is a Novell NetWare protocol that is used with Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) to enable file and print servers to advertise their availability to clients on a network.
-
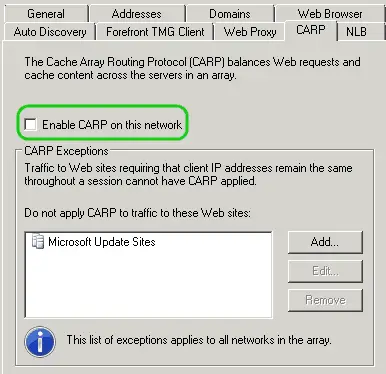
Caching Array Routing Protocol (CARP)
Caching Array Routing Protocol, also known as CARP, is a protocol developed by Microsoft and implemented in Microsoft Proxy Server that allows multiple proxy servers to be arrayed as a single logical cache for distributed content caching.
-

NetWare Protocols
NetWare protocols are the group of protocols developed for and specific to the Novell NetWare network operating system (NOS); popularized in NetWare versions 2 and 3. Some of the networking architecture of NetWare protocols evolved from the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) created in the late 1970s.
-
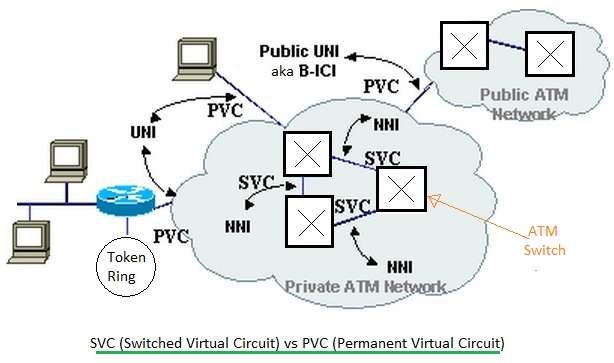
Navigating Switched Virtual Circuits: The SVC Guide
Switched Virtual Circuit, also known as SVC, is a form of telecommunications service that provides a path between two nodes in a packet-switched network.