Our Latest Articles
-
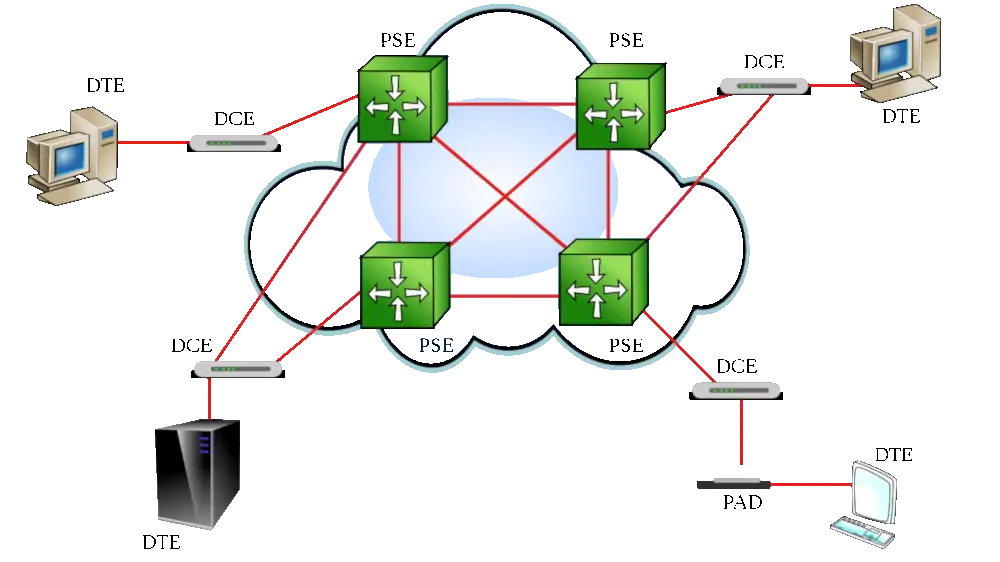
X.25 Protocol
X.25 is a packet-switching protocol for wide area network (WAN) connectivity that uses a public data network (PDN) that parallels the voice network of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
-

World Wide Web Publishing Service
World Wide Web Publishing Service is a component of Internet Information Services (IIS) on Microsoft Windows Server Operating Systems that allows users to publish Web content for use on the Internet.
-
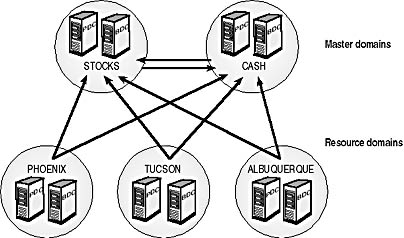
NTDS: From Windows NT Directory Services to NTDS.DIT
Dive deep into the evolution of NTDS, exploring both the historical Windows NT Directory Services and the pivotal NTDS.DIT file in modern Active Directory environments.
-
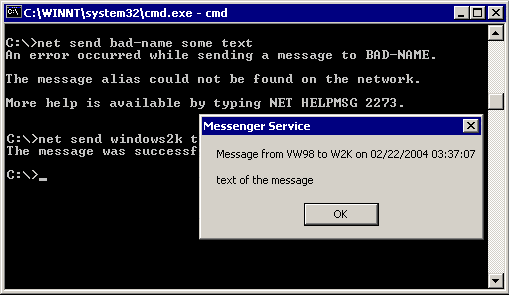
Windows NT Command
Windows NT command is a command that can be typed at the Microsoft Windows NT command prompt, usually to perform an administrative action.
-
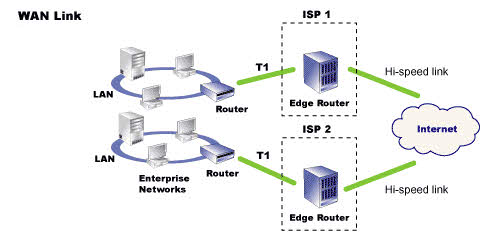
WAN Link
WAN link is a communication circuit that joins two or more local area networks (LANs) into a wide area network (WAN).
-

Virtual Circuit: Bridging Nodes in the Digital Age
Virtual Circuit is a logical path between nodes in a network, typically a telecommunications network.
-
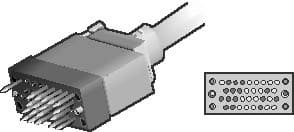
V.35: Understanding the High-Speed Serial Transmission Standard
Explore V.35, the serial transmission standard known for its extended distance support and high-speed data transfer capabilities.
-
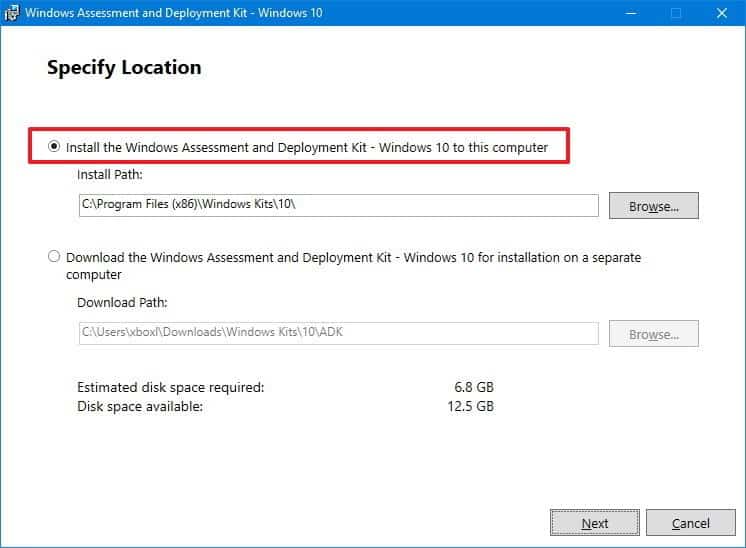
Unattended Installation
Unattended installation is a procedure for installing software without user intervention.
-

TDMA Explained: From Basics to 5G Evolution
Time Division Multiple Access, or TDMA, is a cellular phone technology based on time-division multiplexing (TDM) techniques.
-

Terminator
Terminator is a device connected to one end of a bus or cable that absorbs signals. Terminators prevent signal reflection, which can produce interference that causes signal loss.
-
TCP Three-Way Handshake: A Comprehensive Guide
TCP three-way handshake is a method of initializing a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) session between two hosts on a TCP/IP network.
